ليسدكسأمفتامين
 | |
 | |
| البيانات السريرية | |
|---|---|
| الأسماء التجارية | تيڤنس، إلڤانس، ڤيڤانس، وغيرها |
| أسماء أخرى | (2S)-2,6-Diamino-N-[(2S)-1-phenylpropan-2-yl]hexanamide N-[(2S)-1-Phenyl-2-propanyl]-L-lysinamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607047 |
| License data |
|
| فئة السلامة أثناء الحمل |
|
| إحتمالية الإدمان | مرتفع[1][2] |
| إحتمالية الإدمان | معتدل |
| مسارات الدواء | عن طريق الفم (كپسولات) |
| رمز ATC | |
| الحالة القانونية | |
| الحالة القانونية |
|
| بيانات الحركية الدوائية | |
| التوافر الحيوي | 96.4%[3] |
| الأيض | Hydrolysis by enzymes in red blood cells initially. Subsequent metabolism follows Amphetamine#Pharmacokinetics. |
| بدء المفعول | 2 س[4][5] |
| Elimination half-life | ≤1 س (prodrug molecule) 9–11 س (dextroamphetamine) |
| Duration of action | 10–12 س[2][4][5] |
| الإخراج | البول: ~2% |
| المعرفات | |
| |
| رقم CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| التركيب | C15H25N3O |
| الكتلة المولية | 263٫39 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
ليسدكسأمفتامين، يُباع تحت الاسم التجاري ڤيڤانس Vyvanse، is a medication that is used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in people over the age of five as well as for moderate to severe binge eating disorder in adults.[1] Lisdexamfetamine is taken by mouth.[1][6] In the United Kingdom it is usually less preferred than methylphenidate.[7] Its effects generally begin within 2 hours and last for up to 12 hours.[1]
Common side effects of lisdexamfetamine include loss of appetite, anxiety, diarrhea, trouble sleeping, irritability, and nausea.[1] Rare but serious side effects include mania, sudden cardiac death in those with underlying heart problems, and psychosis.[1] It has a high potential for abuse per the DEA.[1][6] Serotonin syndrome may occur if used with certain other medications.[1] Its use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby and use during breastfeeding is not recommended by the manufacturer.[7][1][6] Lisdexamfetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that works after being converted by the body into dextroamphetamine.[1][8] Chemically, lisdexamfetamine is composed of the amino acid L-lysine, attached to dextroamphetamine.[9]
Lisdexamfetamine was approved for medical use in the United States in 2007.[1] A month supply in the United Kingdom costs the British National Health Service about US$58٫00 اعتبارا من 2019[تحديث][7] In the United States, the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$264.[10] In 2016, it was the 99th most prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 7 million prescriptions.[11] It is a Schedule II controlled substance in the United Kingdom and a Schedule II controlled substance in the United States.[7][12]
الاستخدامات
الطبية
Lisdexamfetamine is used primarily as a treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and binge eating disorder;[13] it has similar off-label uses as those of other pharmaceutical amphetamines.[2] Individuals over the age of 65 were not commonly tested in clinical trials of lisdexamfetamine for ADHD.[13]
تحسين الأداء
موانع الاستخدام
Pharmaceutical lisdexamfetamine dimesylate is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or any of the formulation's inactive ingredients.[13] It is also contraindicated in patients who have used a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) within the last 14 days.[13][14] Amphetamine products are contraindicated by the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) in people with a history of drug abuse, heart disease, or severe agitation or anxiety, or in those currently experiencing arteriosclerosis, glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, or severe hypertension.[15] The USFDA advises anyone with bipolar disorder, depression, elevated blood pressure, liver or kidney problems, mania, psychosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, seizures, thyroid problems, tics, or Tourette syndrome to monitor their symptoms while taking amphetamine.[15] Amphetamine is classified in US pregnancy category C.[15] This means that detriments to the fetus have been observed in animal studies and adequate human studies have not been conducted; amphetamine may still be prescribed to pregnant women if the potential benefits outweigh the risks.[16] Amphetamine has also been shown to pass into breast milk, so the USFDA advises mothers to avoid breastfeeding when using it.[15] Due to the potential for stunted growth, the USFDA advises monitoring the height and weight of children and adolescents prescribed amphetamines.[15] Prescribing information approved by the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration further contraindicates anorexia.[17]
الآثار الجانبية
Products containing lisdexamfetamine have a comparable drug safety profile to those containing amphetamine.[9]
الجرعة الزائدة
التداخلات الدوائية
- Acidifying Agents: Drugs that acidify the urine, such as ascorbic acid, increase urinary excretion of dextroamphetamine, thus decreasing the half-life of dextroamphetamine in the body.[13][18]
- Alkalinizing Agents: Drugs that alkalinize the urine, such as sodium bicarbonate, decrease urinary excretion of dextroamphetamine, thus increasing the half-life of dextroamphetamine in the body.[13][18]
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: Concomitant use of MAOIs and central nervous system stimulants such as lisdexamfetamine can cause a hypertensive crisis.[13]
علم الصيدلة
آلية العمل
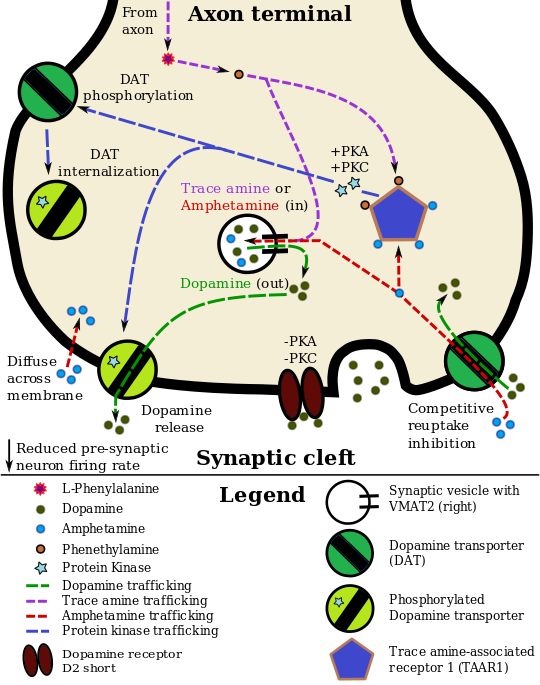
الديناميكية الدوائية للأمفيتامين في العصبو الدوپاميني
|
Lisdexamfetamine is an inactive prodrug that is converted in the body to dextroamphetamine, a pharmacologically active compound which is responsible for the drug's activity.[26] After oral ingestion, lisdexamfetamine is broken down by enzymes in red blood cells to form L-lysine, a naturally occurring essential amino acid, and dextroamphetamine.[13] The conversion of lisdexamfetamine to dextroamphetamine is not affected by gastrointestinal pH and is unlikely to be affected by alterations in normal gastrointestinal transit times.[13][27]
The optical isomers of amphetamine, i.e., dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine, are TAAR1 agonists and vesicular monoamine transporter 2 inhibitors that can enter monoamine neurons;[19][20] this allows them to release monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, among others) from their storage sites in the presynaptic neuron, as well as prevent the reuptake of these neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft.[19][20]
Lisdexamfetamine was developed with the goal of providing a long duration of effect that is consistent throughout the day, with reduced potential for abuse. The attachment of the amino acid lysine slows down the relative amount of dextroamphetamine available to the blood stream. Because no free dextroamphetamine is present in lisdexamfetamine capsules, dextroamphetamine does not become available through mechanical manipulation, such as crushing or simple extraction. A relatively sophisticated biochemical process is needed to produce dextroamphetamine from lisdexamfetamine.[27] As opposed to Adderall, which contains roughly equal parts of racemic amphetamine and dextroamphetamine salts, lisdexamfetamine is a single-enantiomer dextroamphetamine formula.[26][28] Studies conducted show that lisdexamfetamine dimesylate may have less abuse potential than dextroamphetamine and an abuse profile similar to diethylpropion at dosages that are FDA-approved for treatment of ADHD, but still has a high abuse potential when this dosage is exceeded by over 100%.[27]
الكيمياء
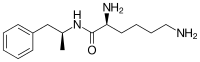
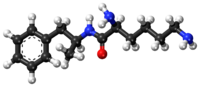
Lisdexamfetamine is a substituted amphetamine with an amide linkage formed by the condensation of dextroamphetamine with the carboxylate group of the essential amino acid L-lysine.[9] The reaction occurs with retention of stereochemistry, so the product lisdexamfetamine exists as a single stereoisomer. There are many possible names for lisdexamfetamine based on IUPAC nomenclature, but it is usually named as N-[(2S)-1-phenyl-2-propanyl]-L-lysinamide or (2S)-2,6-diamino-N-[(1S)-1-methyl-2-phenylethyl]hexanamide.[29] The condensation reaction occurs with loss of water:
- (S)-PhCH 2CH(CH 3)NH 2 + (S)-HOOCCH(NH 2)CH 2CH 2CH 2CH 2NH 2 → (S,S)-PhCH 2CH(CH 3)NHC(O)CH(NH 2)CH 2CH 2CH 2CH 2NH 2 + H 2O
Amine functional groups are vulnerable to oxidation in air and so pharmaceuticals containing them are usually formulated as salts where this moiety has been protonated. This increases stability, water solubility, and, by converting a molecular compound to an ionic compound, increases the melting point and thereby ensures a solid product.[30] In the case of lisdexamfetamine, this is achieved by reacting with two equivalents of methanesulfonic acid to produce the dimesylate salt, a water-soluble (792 mg mL−1) powder with a white to off-white color.[13]
- PhCH 2CH(CH 3)NHC(O)CH(NH 2)CH 2CH 2CH 2CH 2NH 2 + 2 CH 3SO 3H → [PhCH 2CH(CH 3)NHC(O)CH(NH+3)CH 2CH 2CH 2CH 2NH+3][CH 3SO−3] 2
مقارنته بتركيبات أخرى
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate is one marketed formulation delivering dextroamphetamine. The following table compares the drug to other amphetamine pharmaceuticals.
| الدواء | التركيبة | الكتلة المولية [note 1] |
قاعدة الأمفيتامين [note 2] |
قاعدة الأمفيتامين في الجرعات المتساوية |
الجرعات بمحتوى قاعدي متساوي [note 3] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (جم/مول) | (النسبة المئوية) | (جرعة 30 مجم) | ||||||||
| الإجمالي | القاعدة | الإجمالي | الدكسترو- | اللـِڤو- | الدكسترو- | اللـِڤو- | ||||
| كبريتات الدكستروأمفيتامين[32][33] | (C9H13N)2•H2SO4 | 368.49
|
270.41
|
73.38%
|
73.38%
|
—
|
22.0 مج
|
—
|
30.0 مج
| |
| كبريتات الأمفيتامين[34] | (C9H13N)2•H2SO4 | 368.49
|
270.41
|
73.38%
|
36.69%
|
36.69%
|
11.0 مجم
|
11.0 مجم
|
30.0 مجم
| |
| أديرال | 62.57%
|
47.49%
|
15.08%
|
14.2 مجم
|
4.5 مجم
|
35.2 مجم
| ||||
| 25% | كبريتات الدكستروأمفيتامين[32][33] | (C9H13N)2•H2SO4 | 368.49
|
270.41
|
73.38%
|
73.38%
|
—
|
|||
| 25% | كبريتات الأمفيتامين [34] | (C9H13N)2•H2SO4 | 368.49
|
270.41
|
73.38%
|
36.69%
|
36.69%
|
|||
| 25% | سكريدات الدكستروأمفيتامين[35] | (C9H13N)2•C6H10O8 | 480.55
|
270.41
|
56.27%
|
56.27%
|
—
|
|||
| 25% | مونوهيدرات أسپارتات الأمفيتامين [36] | (C9H13N)•C4H7NO4•H2O | 286.32
|
135.21
|
47.22%
|
23.61%
|
23.61%
|
|||
| ديميسيلات الليزديكسامفيتامين[13] | C15H25N3O•(CH4O3S)2 | 455.49
|
135.21
|
29.68%
|
29.68%
|
—
|
8.9 mg
|
—
|
74.2 mg
| |
| معلق الأمفيتامين القاعدي[37] | C9H13N | 135.21
|
135.21
|
100%
|
76.19%
|
23.81%
|
22.9 مجم
|
7.1 مجم
|
22.0 مجم
| |
التاريخ والمجتمع والثقافة
Lisdexamfetamine was developed by New River Pharmaceuticals, who were bought by Takeda Pharmaceuticals through its acquisition of Shire Pharmaceuticals, shortly before it began being marketed. It was developed with the intention of creating a longer-lasting and less-easily abused version of dextroamphetamine, as the requirement of conversion into dextroamphetamine via enzymes in the red blood cells delays its onset of action, regardless of the route of administration.[38]
On 23 April 2008, the FDA approved lisdexamfetamine for treatment of ADHD in adults.[39] On 19 February 2009, Health Canada approved 30 mg and 50 mg capsules of lisdexamfetamine for treatment of ADHD.[40]
In January 2015, lisdexamfetamine was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treatment of binge eating disorder in adults.[41]
Production quotas for 2016 in the United States were 29,750 kilograms.[42]
الأسماء
Lisdexamfetamine is a contraction of L-lysine-dextroamphetamine.
As of July 2014 lisdexamfetamine was sold under the following brands: Elvanse, Samexid, Tyvense, Venvanse, and Vyvanse.[43]
الأبحاث
الاكتئاب
Some clinical trials that used lisdexamfetamine as an add-on therapy with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) for treatment-resistant depression indicated that this is no more effective than the use of an SSRI or SNRI alone.[44] Other studies indicated that psychostimulants potentiated antidepressants, and were under-prescribed for treatment resistant depression. In those studies patients showed significant improvement in energy, mood, and psychomotor activity.[45] In February 2014, Shire announced that two late-stage clinical trials had shown that Vyvanse was not an effective treatment for depression.[46]
الهوامش
- ^ من أجل التوحيد، حُسبت الكتل المولية باستخدام حاسبة الوزن الجزيئي[31] وكانت في حدود 0.01 جم/مول من القيم الصيدلانية المنشورة.
- ^ النسبة المئوية لقاعدة الأمفيتامين = الكتلة الموليةالقاعدية / الكتلة الموليةالإجمالية . النسبة المئوية لقاعدة الأمفيتامين في الأديرال = مجموع النسب المئوية للمكونات / 4.
- ^ dose = (1 / النسبة المئوية لقاعدة الأمفيتامين) &المرات؛ عامل القياس = (الكتلة المولية الإجمالية / الكتلة الموليةالقاعدية) &المرات؛ عامل القياس. تم قياس القيم في هذا العمود على أساس جرعة 30 مجم من كبريتات الدكستروأمفيتامين. نظرًا للاختلافات الدوائية بين هذه الأدوية (على سبيل المثال، الاختلافات في الإطلاق، والامتصاص، والتحويل، والتركيز، والتأثيرات المختلفة للنظائر المتماثلة، ونصف العمر، وما إلى ذلك)، لا ينبغي اعتبار القيم المدرجة جرعات متساوية الفعالية.
- Image legend
الحواشي
المصادر
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ ر ز "Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com (in الإنجليزية). American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 15 April 2019.
- ^ أ ب ت Stahl SM (March 2017). "Lisdexamfetamine". Prescriber's Guide: Stahl's Essential Psychopharmacology (6th ed.). Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. pp. 379–384. ISBN 9781108228749.
- ^ "Public Assessment Report Decentralised Procedure" (PDF). MHRA. p. 14. Retrieved 23 August 2014.
- ^ أ ب Millichap JG (2010). "Chapter 9: Medications for ADHD". In Millichap JG (ed.). Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Handbook: A Physician's Guide to ADHD (2nd ed.). New York, USA: Springer. p. 112. ISBN 9781441913968.
Table 9.2 Dextroamphetamine formulations of stimulant medication
Dexedrine [Peak:2–3 h] [Duration:5–6 h] ...
Adderall [Peak:2–3 h] [Duration:5–7 h]
Dexedrine spansules [Peak:7–8 h] [Duration:12 h] ...
Adderall XR [Peak:7–8 h] [Duration:12 h]
Vyvanse [Peak:3–4 h] [Duration:12 h] - ^ أ ب Brams M, Mao AR, Doyle RL (September 2008). "Onset of efficacy of long-acting psychostimulants in pediatric attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Postgrad. Med. 120 (3): 69–88. doi:10.3810/pgm.2008.09.1909. PMID 18824827.
Onset of efficacy was earliest for d-MPH-ER at 0.5 hours, followed by d, l-MPH-LA at 1 to 2 hours, MCD at 1.5 hours, d, l-MPH-OR at 1 to 2 hours, MAS-XR at 1.5 to 2 hours, MTS at 2 hours, and LDX at approximately 2 hours. ... MAS-XR, and LDX have a long duration of action at 12 hours postdose
- ^ أ ب ت "Lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- ^ أ ب ت ث British national formulary: BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 348–349. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ Heal DJ, Smith SL, Gosden J, Nutt DJ (June 2013). "Amphetamine, past and present – a pharmacological and clinical perspective". J. Psychopharmacol. 27 (6): 479–496. doi:10.1177/0269881113482532. PMC 3666194. PMID 23539642.
- ^ أ ب ت Blick SK, Keating GM (2007). "Lisdexamfetamine". Paediatric Drugs. 9 (2): 129–135, discussion 136–138. doi:10.2165/00148581-200709020-00007. PMID 17407369.
- ^ "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2019". clincalc.com. Retrieved 22 December 2018.
- ^ Drugs of Abuse (PDF). Drug Enforcement Administration • U.S. Department of Justice. 2017. p. 22. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ ر ز "Vyvanse Prescribing Information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. Shire US Inc. May 2017. pp. 17–21. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ^ Heedes G; Ailakis J. "Amphetamine (PIM 934)". INCHEM. International Programme on Chemical Safety. Retrieved 24 June 2014.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج "Adderall XR Prescribing Information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. Shire US Inc. December 2013. pp. 4–6. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ "FDA Pregnancy Categories" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. 21 أكتوبر 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 ديسمبر 2010. Retrieved 31 أكتوبر 2013.
- ^ "Dexamphetamine tablets". Therapeutic Goods Administration. Retrieved 12 April 2014.
- ^ أ ب "Adderall XR Prescribing Information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. Shire US Inc. December 2013. pp. 8–10. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ Miller GM (January 2011). "The emerging role of trace amine-associated receptor 1 in the functional regulation of monoamine transporters and dopaminergic activity". J. Neurochem. 116 (2): 164–176. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07109.x. PMC 3005101. PMID 21073468. خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صالح؛ الاسم "Miller" معرف أكثر من مرة بمحتويات مختلفة. - ^ أ ب ت ث Eiden LE, Weihe E (January 2011). "VMAT2: a dynamic regulator of brain monoaminergic neuronal function interacting with drugs of abuse". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1216 (1): 86–98. Bibcode:2011NYASA1216...86E. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05906.x. PMC 4183197. PMID 21272013.
VMAT2 is the CNS vesicular transporter for not only the biogenic amines DA, NE, EPI, 5-HT, and HIS, but likely also for the trace amines TYR, PEA, and thyronamine (THYR) ... [Trace aminergic] neurons in mammalian CNS would be identifiable as neurons expressing VMAT2 for storage, and the biosynthetic enzyme aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC). ... AMPH release of DA from synapses requires both an action at VMAT2 to release DA to the cytoplasm and a concerted release of DA from the cytoplasm via "reverse transport" through DAT.
خطأ استشهاد: وسم<ref>غير صالح؛ الاسم "E Weihe" معرف أكثر من مرة بمحتويات مختلفة. - ^ Sulzer D, Cragg SJ, Rice ME (August 2016). "Striatal dopamine neurotransmission: regulation of release and uptake". Basal Ganglia. 6 (3): 123–148. doi:10.1016/j.baga.2016.02.001. PMC 4850498. PMID 27141430.
Despite the challenges in determining synaptic vesicle pH, the proton gradient across the vesicle membrane is of fundamental importance for its function. Exposure of isolated catecholamine vesicles to protonophores collapses the pH gradient and rapidly redistributes transmitter from inside to outside the vesicle. ... Amphetamine and its derivatives like methamphetamine are weak base compounds that are the only widely used class of drugs known to elicit transmitter release by a non-exocytic mechanism. As substrates for both DAT and VMAT, amphetamines can be taken up to the cytosol and then sequestered in vesicles, where they act to collapse the vesicular pH gradient.
- ^ Ledonne A, Berretta N, Davoli A, Rizzo GR, Bernardi G, Mercuri NB (July 2011). "Electrophysiological effects of trace amines on mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons". Front. Syst. Neurosci. 5: 56. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2011.00056. PMC 3131148. PMID 21772817.
Three important new aspects of TAs action have recently emerged: (a) inhibition of firing due to increased release of dopamine; (b) reduction of D2 and GABAB receptor-mediated inhibitory responses (excitatory effects due to disinhibition); and (c) a direct TA1 receptor-mediated activation of GIRK channels which produce cell membrane hyperpolarization.
- ^ "TAAR1". GenAtlas. University of Paris. 28 January 2012. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
• tonically activates inwardly rectifying K(+) channels, which reduces the basal firing frequency of dopamine (DA) neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTA)
- ^ Underhill SM, Wheeler DS, Li M, Watts SD, Ingram SL, Amara SG (July 2014). "Amphetamine modulates excitatory neurotransmission through endocytosis of the glutamate transporter EAAT3 in dopamine neurons". Neuron. 83 (2): 404–416. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.043. PMC 4159050. PMID 25033183.
AMPH also increases intracellular calcium (Gnegy et al., 2004) that is associated with calmodulin/CamKII activation (Wei et al., 2007) and modulation and trafficking of the DAT (Fog et al., 2006; Sakrikar et al., 2012). ... For example, AMPH increases extracellular glutamate in various brain regions including the striatum, VTA and NAc (Del Arco et al., 1999; Kim et al., 1981; Mora and Porras, 1993; Xue et al., 1996), but it has not been established whether this change can be explained by increased synaptic release or by reduced clearance of glutamate. ... DHK-sensitive, EAAT2 uptake was not altered by AMPH (Figure 1A). The remaining glutamate transport in these midbrain cultures is likely mediated by EAAT3 and this component was significantly decreased by AMPH
- ^ Vaughan RA, Foster JD (September 2013). "Mechanisms of dopamine transporter regulation in normal and disease states". Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 34 (9): 489–496. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2013.07.005. PMC 3831354. PMID 23968642.
AMPH and METH also stimulate DA efflux, which is thought to be a crucial element in their addictive properties [80], although the mechanisms do not appear to be identical for each drug [81]. These processes are PKCβ– and CaMK–dependent [72, 82], and PKCβ knock-out mice display decreased AMPH-induced efflux that correlates with reduced AMPH-induced locomotion [72].
- ^ أ ب "Identification". Lisdexamfetamine. University of Alberta. 16 September 2013. Retrieved 13 June 2014.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ أ ب ت Jasinski DR, Krishnan S (June 2009). "Abuse liability and safety of oral lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in individuals with a history of stimulant abuse". J. Psychopharmacol. (Oxford). 23 (4): 419–427. doi:10.1177/0269881109103113. PMID 19329547.
- ^ "Adderall XR Prescribing Information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. pp. 1–18. Retrieved 7 October 2013.
- ^ "Lidsexamfetamine". ChemSpider. Royal Society of Chemistry. 2015. Retrieved April 22, 2019.
- ^ Stahl, P. Heinrich; Wermuth, Camille G., eds. (2011). Pharmaceutical Salts: Properties, Selection, and Use (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-3-90639-051-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editorlink2=ignored (|editor-link2=suggested) (help) - ^ "Molecular Weight Calculator". Lenntech. Retrieved 19 August 2015.
- ^ أ ب "Dextroamphetamine Sulfate USP". Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. March 2014. Retrieved 19 August 2015.
- ^ أ ب "D-amphetamine sulfate". Tocris. 2015. Retrieved 19 August 2015.
- ^ أ ب "Amphetamine Sulfate USP". Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. March 2014. Retrieved 19 August 2015.
- ^ "Dextroamphetamine Saccharate". Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. March 2014. Retrieved 19 August 2015.
- ^ "Amphetamine Aspartate". Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. March 2014. Retrieved 19 August 2015.
- ^ Mattingly, G (May 2010). "Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate: a prodrug stimulant for the treatment of ADHD in children and adults". CNS Spectrums. 15 (5): 315–25. doi:10.1017/S1092852900027541. PMID 20448522.
- ^ "FDA Adult Approval of Vyvanse – FDA Label and Approval History" (PDF).
- ^ Health Canada Notice of Compliance – Vyvanse[dead link]. 19 February 2009, retrieved on 9 March 2009.
- ^ "Press Announcements – FDA expands uses of Vyvanse to treat binge-eating disorder". FDA (in الإنجليزية). 30 January 2015.
- ^ "DEA Office of Diversion Control" (PDF). DEA. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ^ "Lisdexamfetamine international brands". Drugs.com. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ^ Dale E, Bang-Andersen B, Sánchez C (May 2015). "Emerging mechanisms and treatments for depression beyond SSRIs and SNRIs". Biochem. Pharmacol. 95 (2): 81–97. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2015.03.011. PMID 25813654.
- ^ Stotz, G.; Woggon, B.; Angst, J. (1999). "Psychostimulants in the therapy of treatment-resistant depression Review of the literature and findings from a retrospective study in 65 depressed patients". Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 1 (3): 165–74. PMC 3181580. PMID 22034135.
- ^ Hirschler, Ben (7 February 2014). "UPDATE 2-Shire scraps Vyvanse for depression after failed trials". Reuters. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
وصلات خارجية
- CS1 errors: periodical ignored
- CS1 errors: unsupported parameter
- Articles with dead external links from December 2017
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Template:drugs.com link with non-standard subpage
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Pages using infobox drug with unknown parameters
- Articles without KEGG source
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- مقالات فيها عبارات متقادمة منذ 2019
- جميع المقالات التي فيها عبارات متقادمة
- RTT
- أمفتامين
- مفقدات الشهية
- منشطات جنسية طبيعية
- Codrugs
- Drugs acting on the cardiovascular system
- أدوية تعمل على الجهاز العصبي
- Ergogenic aids
- مسببات الابتهاج
- Excitatory amino acid reuptake inhibitors
- محسنات الذهن
- Norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents
- فينيثيلامينات
- منبهات
- أمفيتامينات مستبدلة
- TAAR1 agonists
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company brands
- علاج اضطراب قصور الإنتباه وفرط الحركة
- VMAT inhibitors
- مواد تحظرها الوكالة العالمية لمكافحة المنشطات