خـِيْ خى
Heihe
黑河市 Хэйхэ | |
|---|---|
 The Amur River (Heilong Jiang) and Heihe | |
 موقع مدينة هـِيْخى (أصفر) في خـِيْلونگجيانگ (رمادي فاتح) | |
| الإحداثيات (Heihe Customs): 50°14′24″N 127°31′16″E / 50.2401°N 127.5210°E | |
| البلد | جمهورية الصين الشعبية |
| المقاطعة | خـِيْلونگجيانگ |
| التقسيمات بمستوى ناحية | 6 |
| مقر البلدية | مديرية آيخوي |
| الحكومة | |
| • النوع | مدينة بمستوى محافظة |
| • CPC Heihe Secretary | Liu Gang (刘刚) |
| • Mayor | Zhang Enliang (张恩亮) |
| المساحة | |
| • مدينة بمستوى محافظة | 54٬390 كم² (21٬000 ميل²) |
| • الحضر | 1٬443 كم² (557 ميل²) |
| • العمران | 1٬443 كم² (557 ميل²) |
| التعداد (2020 census)[1] | |
| • مدينة بمستوى محافظة | 1٬286٬401 |
| • الكثافة | 24/km2 (61/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 223٬832 |
| • الكثافة الحضرية | 160/km2 (400/sq mi) |
| • العمرانية | 223٬832 |
| • الكثافة العمرانية | 160/km2 (400/sq mi) |
| منطقة التوقيت | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 164300 |
| مفتاح الهاتف | 0456 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HL-11 |
| Licence plates | 黑N |
| Climate | Dwb |
| الموقع الإلكتروني | www |
| خـِيْ خى | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Heihe", as written in Chinese | |||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||
| الصينية | 黑河 | ||||||
| المعنى الحرفي | black river | ||||||
| |||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||
| Manchu script | ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ ᡠᠯᠠ ᡥᠣᡨᠣᠨ | ||||||
| Romanization | Sahaliyan'ula hoton | ||||||
| Russian name | |||||||
| Russian | Хэйхэ | ||||||
| Aigun | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||
| الصينية المبسطة | 瑷珲 | ||||||
| الصينية التقليدية | 璦琿 | ||||||
| البريد | Aigun | ||||||
| |||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||
| Manchu script | ᠠᡳ᠌ᡥᡡᠨ ᡥᠣᡨᠣᠨ | ||||||
| Romanization | Aigun hoton | ||||||
| Russian name | |||||||
| Russian | Айгунь | ||||||
خـِيْ خى أو هـِيْخى (الصينية: 黑河; پنين: Hēihé؛ حرفياً 'النهر الأسود'؛ بالروسية: Хэйхэ) هي مدينة بمستوى محافظة في مقاطعة خـِيْلونگجيانگ في شمال الصين، وتقع على الحدود الروسية، على الضفة الجنوبية لنهر آمور (خـِيْلونگ)، عبر النهر من بلاگوڤيشينسك. وفي تعداد 2020، كان هناك 1,286,401 نسمة يقطنون المدينة بمستوى محافظة، منهم 223,832 نسمة يعيشون في المنطقة الحضرية (أو العمرانية) التي تشكل مديرية آيخوي.
هـِيْخى هي المحطة النهائية في الشمال الشرقي لـخط هـِيْخى-تنگتشونگ القطري، الذي يُستخدم أحياناً ليقسم الصين إلى شرق وغرب.
التاريخ
Heihe, formerly Aihui or Aigun, is one of the five oldest cities in Heilongjiang, along with Tsitsihar, Yilan, Acheng and Hulan. Human beings started to settle in Heihe region as early as the Paleolithic Age.[2] Later it became home to local tribes. During the Qing Dynasty, Heihe was the first place troops sent to Heilongjiang were stationed. The predecessor of today's Heihe was the town established by the indigenous Ducher people of the Amur Valley in the mid 1650s.[2] It was established some 30 km (19 mi) south of the modern city site[3] (in today's Aihui District) and was known as Aigun, Heilongjiang, or Saghalien Ula. (The two last names both mean "the Black Dragon River" - the name for the Amur River in Chinese and Manchu, respectively).
After the Ducher were evacuated by the Qing to the Sungari or Hurka in the 1650s, the Ducher town was probably vacated. However, in 1683-85 the Manchus re-used the site as a base for their campaign against the Russian fort of Albazin.[4] Aigun was the capital (the seat of the military governor) of Heilongjiang from 1683 to 1690, before the capital was moved to Nenjiang (Mergen).[5] After the capture of Albazin in 1685 or 1686, the Qing governor relocated the town to a new site on the right (southwestern) bank of the Amur, about 3 miles downstream from the original.[6][7] The new site occupied the location of the former village of the Daurian chief named Tolga.[6] The city became known primarily under its Manchu name Saghalien Ula hoton (Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ
ᡠᠯᠠ
ᡥᠣᡨᠣᠨ sahaliyan ula hoton) and Chinese name Heilongjiang Cheng (黑龍江城), which both mean "Black River City".[8] Later the governor office was transferred to Qiqihar. However, Aigun remained the seat of the Deputy Lieutenant-General (Fu dutong), responsible for a large district covering much of the Amur Valley within the province of Heilongjiang as it existed in those days.[5]
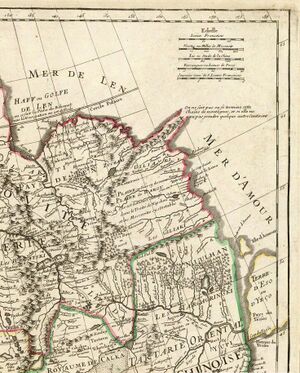
Aigun was visited around 1709 as a part of a nationwide Sino-French cartographic program by the Jesuits Jean-Baptiste Régis, Pierre Jartoux, and Xavier Ehrenbert Fridelli,[9] who found it a stronghold, serving as the base of Manchus controlling the Amur River basin. The Aigun Treaty was concluded at Aigun in 1858. According to this treaty, the left bank of the Amur River was conceded to Czarist Russia.
After the Xinhai Revolution, Aigun became the county seat of the newly created Aigun County by the Republic of China. On November 15, 1980, Heihe City was established, administering two county-level cities and three counties including Beian, Wudalianchi, Nenjiang, Sunwu and Sunke. Aihui County was abolished, being merged into the Heihe City.[10]
الجغرافيا
Heihe is located at the South bank of the Amur, opposite to the city of Blagoveshchensk in Russia's Amur Oblast. Its jurisdictional area stretches for 54،390 km2 (21،000 sq mi), which spans from 124° 45' to 129° 18' E longitude and 47° 42' to 51° 03' N latitude. Domestically, Heihe City borders Da Hinggan Ling Prefecture to the north, Yichun to the southeast, Suihua to the south, Qiqihar to the southwest, and Hulunbuir (Inner Mongolia) to the west. The Amur has formed the Sino-Russian border since the 1858 Aigun Treaty and 1860 Treaty of Peking. The area north of the Amur had previously belonged to Imperial China.
المناخ
Heihe experiences a monsoon-influenced humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dwb), but Dwa in the south of the prefecture, with long, bitterly cold, windy, but dry winters due to the influence of the Siberian high, and warm, wet summers, due to the East Asian monsoon. Based on data from 1981 to 2010, the monthly daily mean temperature in January, the coldest month, is −22.0 °C (−7.6 °F), and July, the warmest month, averages 21.1 °C (70.0 °F), with an average annual temperature +0.92 °C (33.7 °F). Close to two-thirds of the annual precipitation falls in the months of June to August. Extreme temperatures have ranged from −44.5 °C (−48 °F) to 39.3 °C (103 °F).
| بيانات المناخ لـ هـِيْخى (مديرية آيخوي، المعتادة 1981–2010، القصوى 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| الشهر | ينا | فب | مار | أبر | ماي | يون | يول | أغس | سبت | أكت | نوف | ديس | السنة |
| القصوى القياسية °س (°ف) | −0.4 (31.3) |
7.1 (44.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
28.3 (82.9) |
35.1 (95.2) |
39.3 (102.7) |
37.2 (99.0) |
35.1 (95.2) |
31.1 (88.0) |
28.2 (82.8) |
12.5 (54.5) |
1.1 (34.0) |
39.3 (102.7) |
| متوسط القصوى اليومية °س (°ف) | −16.3 (2.7) |
−10.3 (13.5) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
10.4 (50.7) |
19.0 (66.2) |
24.9 (76.8) |
26.5 (79.7) |
24.3 (75.7) |
18.3 (64.9) |
8.4 (47.1) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−15.3 (4.5) |
6.9 (44.5) |
| المتوسط اليومي °س (°ف) | −22.0 (−7.6) |
−17.2 (1.0) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
4.2 (39.6) |
12.4 (54.3) |
18.7 (65.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
18.8 (65.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
2.4 (36.3) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
−20.5 (−4.9) |
0.9 (33.7) |
| متوسط الدنيا اليومية °س (°ف) | −26.5 (−15.7) |
−22.7 (−8.9) |
−13.8 (7.2) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
5.5 (41.9) |
12.4 (54.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
13.9 (57.0) |
6.4 (43.5) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
−15.6 (3.9) |
−24.7 (−12.5) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
| الصغرى القياسية °س (°ف) | −44.5 (−48.1) |
−40.9 (−41.6) |
−32.8 (−27.0) |
−19.1 (−2.4) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
1.7 (35.1) |
7.9 (46.2) |
4.0 (39.2) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
−19.1 (−2.4) |
−32.8 (−27.0) |
−38.9 (−38.0) |
−44.5 (−48.1) |
| متوسط تساقط الأمطار mm (inches) | 4.1 (0.16) |
3.0 (0.12) |
5.7 (0.22) |
25.2 (0.99) |
41.1 (1.62) |
86.0 (3.39) |
131.0 (5.16) |
121.4 (4.78) |
65.4 (2.57) |
23.5 (0.93) |
9.1 (0.36) |
6.3 (0.25) |
521.8 (20.55) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 7.1 | 4.3 | 4.8 | 8.0 | 10.4 | 13.4 | 14.0 | 13.8 | 11.8 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 8.7 | 130.0 |
| متوسط الرطوبة النسبية (%) | 68 | 63 | 56 | 53 | 53 | 67 | 77 | 79 | 71 | 60 | 65 | 69 | 65 |
| متوسط نقطة الندى °س (°ف) | −27 (−17) |
−24 (−11) |
−15 (5) |
−7 (19) |
3 (37) |
13 (55) |
17 (63) |
15 (59) |
6 (43) |
−5 (23) |
−15 (5) |
−25 (−13) |
−5 (22) |
| Mean monthly ساعات سطوع الشمس | 139.5 | 194.9 | 226.3 | 222.0 | 251.1 | 255.0 | 226.3 | 226.3 | 168.0 | 189.1 | 156.0 | 124.0 | 2٬378٫5 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration,[11] Weather China (Precipitation days 1971–2000)[12] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Blagoveshchensk (Snow days 1981–2010, Sun 1961–1990)[13][14]
Source 3: Time and Date (dewpoints, between 2005-2015)[15] | |||||||||||||
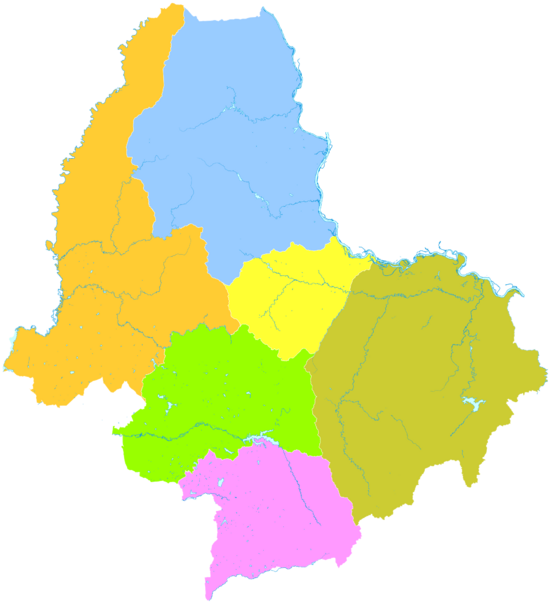
التقسيمات الإدارية
| الاسم | Hanzi | هانيو پنين | التعداد (تقدير 2010) | المساحة (كم²) | الكثافة (/كم²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| مديرية آيخوي | 爱辉区 | Àihuī Qū | 211,313 | 13,993 | 15.1 |
| Bei'an city | 北安市 | Běi'ān Shì | 436,444 | 6,313 | 69.1 |
| Wudalianchi city | 五大连池市 | Wǔdàliánchí Shì | 326,390 | 9,800 | 33.3 |
| Nenjiang city | 嫩江市 | Nènjiāng shì | 495,519 | 15,360 | 32.3 |
| Xunke County | 逊克县 | Xùnkè Xiàn | 101,411 | 17,020 | 6.0 |
| Sunwu County | 孙吴县 | Sūnwú Xiàn | 102,821 | 4,454 | 23.1 |
النقل
النقل إلى ومن هـِيْخى هو كالتالي:
- الطرق السريعة
- China National Highway 202: Heihe–Dalian via Harbin, Jilin City and Shenyang
- Provincial highways: Heihe–Mohe, etc.
- Blagoveshchensk–Heihe Bridge, completed at the end of 2019, is a 2-lane highway bridge over the Amur to link Blagoveshchensk and Heihe.
- Railway (China Railway): Heihe–Bei'an to Harbin, Qiqihar and Daqing
- Air: Heihe Aihui Airport
The world's first international cable car to Blagoveshchensk has also been proposed to open in 2022.[16][17]
الطاقة
West of Heihe, there is an HVDC back-to-back station for realizing an interconnection between the power grids of Russia and China with 750 MW transmission capacity.[citation needed]
السياحة
Heihe has plenty of natural tourism resources, including the Amur River and Wudalianchi Lake and Wudalianchi Volcanic Range, where people can take a trip to local volcanoes. The Old City of Aigun is a famous historical scenic spot, in which the Treaty of Aigun between China and Russia was signed in the 19th century.
الرياضة
Heihe University (黑河学院) has requested the Russian bandy club SKA Neftyanik to send a coach, offering a one-year contract.[1]
المدن الشقيقة
 بلاگوڤيشينسك، أوبلاست آمور، روسيا
بلاگوڤيشينسك، أوبلاست آمور، روسيا كراسنويارسك، كراي كراسنويارسك، روسيا[18]
كراسنويارسك، كراي كراسنويارسك، روسيا[18] ياكوتسك، جمهورية ساخا، روسيا
ياكوتسك، جمهورية ساخا، روسيا
انظر أيضاً
المراجع
- ^ "China: Hēilóngjiāng (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map". Citypopulation.de. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ أ ب Амурская область: История НАРОДЫ АМУРСКОЙ ЗЕМЛИ Archived 2011-07-18 at the Wayback Machine (Amur Oblast: the History. The peoples of the Amur Land) (in روسية)
- ^ The Ancient City of Aigun Archived 2009-10-29 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bruce Mancall, 'Russia and China: Their Diplomatic Relations to 1728, 1971, pages 115-127
- ^ أ ب Edmonds, Richard Louis (1985). Northern Frontiers of Qing China and Tokugawa Japan: A Comparative Study of Frontier Policy. University of Chicago, Department of Geography; Research Paper No. 213. pp. 115–117. ISBN 0-89065-118-3.
- ^ أ ب E.G.Ravenstein, The Russians on the Amur. London, 1861. text can be found on Google Books. Pages 18,48.
- ^ The Jesuits (at du Halde, pp. 18-19), who visited the "new" Aigun ca. 1709, mentioned the old site on the left bank of the river (which they called Aykom), but said that it was 13 li, i.e., some 8.3 km, upstream from the new site. They also claimed that Aykom was founded by the 15th-century Ming Yongle Emperor but abandoned within 20 years. Although Yongle's Amur expeditions are well known (see, e.g., Yishiha), there seem to be no corroboration in modern literature for the existence of a Yongle-era fort at the Old Aigun site.
- ^ Jean-Baptiste Du Halde, Description géographique, historique, chronologique, politique, et physique de l'empire de la Chine et de la Tartarie chinoise, enrichie des cartes générales et particulieres de ces pays, de la carte générale et des cartes particulieres du Thibet, & de la Corée; & ornée d'un grand nombre de figures & de vignettes gravées en tailledouce, Vol. 4 (La Haye: H. Scheurleer, 1736). Pp. 18-19.
- ^ Jean-Baptiste Du Halde, Description géographique, historique, chronologique, politique, et physique de l'empire de la Chine et de la Tartarie chinoise, enrichie des cartes générales et particulieres de ces pays, de la carte générale et des cartes particulieres du Thibet, & de la Corée; & ornée d'un grand nombre de figures & de vignettes gravées en tailledouce, Vol. 1 (La Haye: H. Scheurleer, 1736). (p. xxxviii in Vol. 1)
- ^ 爱辉区概况 (in Chinese (China)). Heihe People's Government. 2007-06-06. Archived from the original on 2012-12-25. Retrieved 2013-12-06.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 - WeatherBk Data (in Chinese (China)). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2020-04-15.
- ^ 黑河 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 (in الصينية المبسطة). Weather China. Retrieved 2012-07-12.
- ^ Климат Благовещенска. Pogoda.
- ^ "Climatological Information for Blagovescensk, Russia". Hong Kong Observatory. Archived from the original on 2018-10-10. Retrieved 2011-10-17.
- ^ "Climate & Weather Averages for Aihui weather station (50468)". Time and Date. Retrieved 4 February 2022.
- ^ Amy Woodyatt. "The world's first cross-border cable car will travel from Russia to China in under 8 minutes". CNN (in الإنجليزية).
- ^ "Russia to China in under eight minutes: World's first cross-border cable car unveiled". www.abc.net.au (in الإنجليزية الأسترالية). 31 July 2019.
- ^ As of today, Krasnoyarsk City Administration has concluded protocols of intent and agreements on cooperation with the following foreign cities:
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Articles with روسية-language sources (ru)
- CS1 uses الصينية-language script (zh)
- CS1 Chinese (China)-language sources (zh-cn)
- CS1 الصينية المبسطة-language sources (zh-hans)
- CS1 uses الروسية-language script (ru)
- CS1 الإنجليزية الأسترالية-language sources (en-au)
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Articles containing صينية-language text
- Articles containing روسية-language text
- Articles containing simplified Chinese-language text
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles containing traditional Chinese-language text
- Articles with unsourced statements from February 2017
- مدن خـِيْلونگجيانگ
- المعابر الحدودية بين روسيا والصين
- تقسيمات بمستوى محافظات في خـِيْلونگجيانگ