فلوريد السترونشيوم
| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| أسماء أخرى
ثنائي فلوريد السترونشيوم
فلوريد السترونشيوم الثنائي | |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.091 |
| رقم EC |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | SrF2 |
| كتلة مولية | 125.62 جم/مول |
| الكثافة | 4.24 جم/سم 3 |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| نقطة الغليان | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | 0.117 جم/100 م.مول |
| نتاج قابلية الذوبان، Ksp | 4.33×10−9[1] |
| القابلية المغناطيسية | −37.2·10−6 سم3/مول |
| معامل الانكسار (nD) | 1.439 @0.58 μm |
| البنية | |
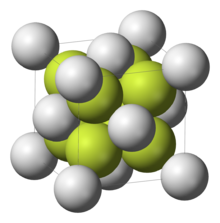
| البنية البلورية | نظام بلوري مكعب، cF12 |
| الزمرة الفراغية | Fm3m, #225 |
| ثابت العقد | a = 5.80 Å, b = 5.80 Å, c = 5.80 Å |
| ثابت العقد | α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 90° |
| Sr, 8, cubic F, 4, tetrahedral | |
| المخاطر | |
| نقطة الوميض | غير قابل للاشتعال |
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |
أنيونات أخرى
|
كلوريد السترونشيوم بروميد السترونشيوم يوديد السترونشيوم |
كاتيونات أخرى
|
فلوريد البريليوم فلوريد المغنسيوم فلوريد الكالسيوم فلوريد الباريوم |
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
فلوريد السترونشيوم (Strontium fluoride، صيغته SrF2، ويسمى أيضاً ثنائي فلوريد السترونشيوم أو فلوريد السترنشيوم الثنائي، هو مادة صلبة بلورية بيضاء هشة تتكون من فلوريد السترنشيوم، يظهر في الطبيعة على شكل معدن السترونشيوفلوريت شديد الندرة.[2][3]
التحضير
يُحضر فلوريد السترونشيوم عن طريق تفاعل حمض الهيدروفلوريك مع كربونات السترونشيوم.[4]
البُنية
The solid adopts the fluorite structure. In the vapour phase the SrF2 molecule is non-linear with an F−Sr−F angle of approximately 120°.[5] This is an exception to VSEPR theory which would predict a linear structure. Ab initio calculations have been cited to propose that contributions from d orbitals in the shell below the valence shell are responsible.[6] Another proposal is that polarization of the electron core of the strontium atom creates an approximately tetrahedral distribution of charge that interacts with the Sr−F bonds.[7]
الخصائص
It is almost insoluble in water (its Ksp value is approximately 2.0x10−10 at 25 degrees Celsius).
It irritates eyes and skin, and is harmful when inhaled or ingested.
Similar to CaF2 and BaF2, SrF2 displays superionic conductivity at elevated temperatures.[8]
Strontium fluoride is transparent to light in the wavelengths from vacuum ultraviolet (150 nm) to infrared (11 μm). Its optical properties are intermediate to calcium fluoride and barium fluoride.[9]
الاستخدامات
يستخدم فلوريد السترونشيوم كمادة بصرية لمجموعة صغيرة من التطبيقات الخاصة، على سبيل المثال، كطلاء بصري على العدسات وأيضاً كبلورة قياس المضيائية الحرارية. يوجد لفلوريد السترنشيوم استخدام آخر وهو كحامل للنظير المشع السترونشيوم-90 في المولدات الكهروحرارية التي تعمل بالنظائر المشعة.
المصادر
- ^ John Rumble (June 18, 2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (in English) (99 ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–189. ISBN 978-1138561632.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Strontiofluorite".
- ^ "List of Minerals". 21 March 2011.
- ^ W. Kwasnik (1963). "Strontium Fluoride". In G. Brauer (ed.). Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Vol. 1. NY, NY: Academic Press. p. 234.
- ^ Greenwood, N. N. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edition ed.). Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Ab initio model potential study of the equilibrium geometry of alkaline earth dihalides: MX2 (M = Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba; X=F, Cl, Br, I)Seijo L.,Barandiarán Z J. Chem. Phys. 94, 3762 (1991) DOI:10.1063/1.459748
- ^ Core Distortions and Geometries of the Difluorides and Dihydrides of Ca, Sr, and Ba Bytheway I, Gillespie RJ, Tang TH, Bader RF Inorganic Chemistry, Vol.34, No.9, 2407-2414, 1995 DOI:10.1021/ic00113a023
- ^ "Newmet Koch - Strontium". Archived from the original on 2005-12-14.
- ^ Mediatopia Ltd. "Strontium Fluoride SrF2". Crystran.com. Retrieved 2025-02-08.