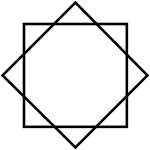
نجمة ثمانية
| Regular octagram | |
|---|---|
 octagram منتظم | |
| النوع | مضلع نجمي منتظم |
| الأضلاع والرؤوس | {{{p8/3-جوانب}}} |
| رمز شلفلي | {{{{p8/3-شلفلي}}}} |
| مخططات كوكستر-دنكن | |
| مجموعة التماثل | ثنائي الأسطح (D{{{p8/3-جوانب}}}) |
| الزاوية الداخلية (الدرجات) | {{{زاوية p8/3}}}° |
| الخصائص | نجمي، دائري، متساوي الأضلاع، متوازي، متجانس الأضلاع |
في الهندسة، النجمة الثمانية octagram، هي مضلع ثماني الرؤوس.
| المضلعات النجمية |
|---|
|
|
تفاصيل
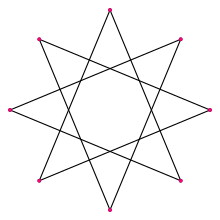
عموماً، an octagram is any self-intersecting octagon (8-sided polygon).
The regular octagram is labeled by the Schläfli symbol {8/3}, which means an 8-sided star, connected by every third point.
تنويعات
These variations have a lower dihedral, Dih4, symmetry:
 Narrow 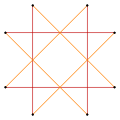 Wide (45 degree rotation) |
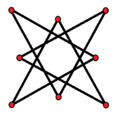  Isotoxal |
 An old Flag of Chile contained this octagonal star geometry with edges removed (the Guñelve). |
 The regular octagonal star is very popular as a symbol of rowing clubs in the Cologne Lowland, as seen on the club flag of the Cologne Rowing Association. |
 The geometry can be adjusted so 3 edges cross at a single point, like the Auseklis symbol |
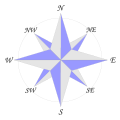 An 8-point compass rose can be seen as an octagonal star, with 4 primary points, and 4 secondary points. |
The symbol Rub el Hizb is a Unicode glyph ۞ at U+06DE.
As a quasitruncated square
Deeper truncations of the square can produce isogonal (vertex-transitive) intermediate star polygon forms with equal spaced vertices and two edge lengths. A truncated square is an octagon, t{4}={8}. A quasitruncated square, inverted as {4/3}, is an octagram, t{4/3}={8/3}.[1]
The uniform star polyhedron stellated truncated hexahedron, t'{4,3}=t{4/3,3} has octagram faces constructed from the cube in this way. It may be considered for this reason as a three-dimensional analogue of the octagram.
| Regular | Quasiregular | Isogonal | Quasiregular |
|---|---|---|---|
 {4} |
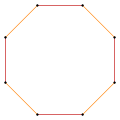 t{4}={8} |
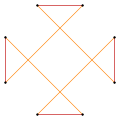
|
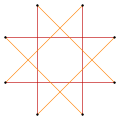 t'{4}=t{4/3}={8/3} |
| Regular | Uniform | Isogonal | Uniform |
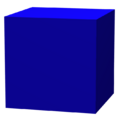 {4,3} |
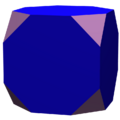 t{4,3} |
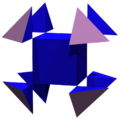
|
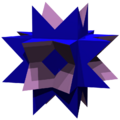 t'{4,3}=t{4/3,3} |
Another three-dimensional version of the octagram is the nonconvex great rhombicuboctahedron (quasirhombicuboctahedron), which can be thought of as a quasicantellated (quasiexpanded) cube, t0,2{4/3,3}.
مركبات مضلعات نجمية
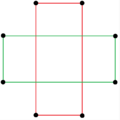
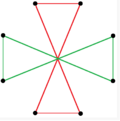
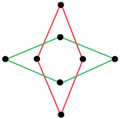
There are two regular octagrammic star figures (compounds) of the form {8/k}, the first constructed as two squares {8/2}=2{4}, and second as four degenerate digons, {8/4}=4{2}. There are other isogonal and isotoxal compounds including rectangular and rhombic forms.
| Regular | Isogonal | Isotoxal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
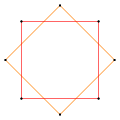 a{8}={8/2}=2{4} |
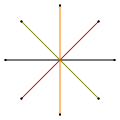 {8/4}=4{2} |
|
|
|
{8/2} or 2{4}, like Coxeter diagrams ![]()
![]()
![]() +
+ ![]()
![]()
![]() , can be seen as the 2D equivalent of the 3D compound of cube and octahedron,
, can be seen as the 2D equivalent of the 3D compound of cube and octahedron, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() +
+ ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , 4D compound of tesseract and 16-cell,
, 4D compound of tesseract and 16-cell, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() +
+ ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() and 5D compound of 5-cube and 5-orthoplex; that is, the compound of a n-cube and cross-polytope in their respective dual positions.
and 5D compound of 5-cube and 5-orthoplex; that is, the compound of a n-cube and cross-polytope in their respective dual positions.
تمثيلات أخرى لنجم مضلع ثماني
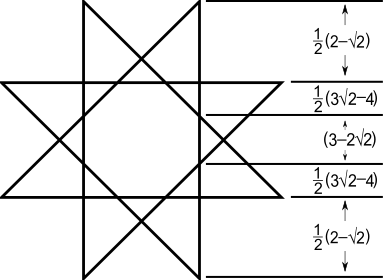
An octagonal star can be seen as a concave hexadecagon, with internal intersecting geometry erased. It can also be dissected by radial lines.
| star polygon | Concave | Central dissections | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
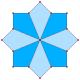
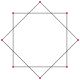 Compound 2{4} |
 |8/2| |
|
|

|
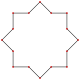
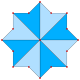
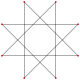 Regular {8/3} |
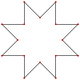 |8/3| |

|

|

|
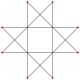 Isogonal |
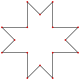
|

|
|
|
 Isotoxal |
|
|

|
|
استخدامات أخرى
- In Unicode, the "Eight Spoked Asterisk" symbol ✳ is U+2733.
انظر أيضا
- الاستخدام
- ربع الحزب – Islamic character
- نجمة عشتار – symbol of the ancient Sumerian goddess Inanna and her East Semitic counterpart Ishtar and Roman Venus.
- نجمة لكشمي – Indian character
- Surya Majapahit – usage during Majapahit times in Indonesia to represent the Hindu gods of the directions
- Compass rose – usage in compasses to represent the cardinal directions for the eight principal winds
- Auseklis – usage of regular octagram by Latvians
- Guñelve – representation of Venus in Mapuche iconography.
- Selburose – usage of regular octagram in Norwegian design
- النجوم عموماً
المصادر
- ^ The Lighter Side of Mathematics: Proceedings of the Eugène Strens Memorial Conference on Recreational Mathematics and its History, (1994), Metamorphoses of polygons, Branko Grünbaum
- Grünbaum, B. and G.C. Shephard; Tilings and Patterns, New York: W. H. Freeman & Co., (1987), ISBN 0-7167-1193-1.
- Grünbaum, B.; Polyhedra with Hollow Faces, Proc of NATO-ASI Conference on Polytopes ... etc. (Toronto 1993), ed T. Bisztriczky et al., Kluwer Academic (1994) pp. 43–70.
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strass, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 26. pp. 404: Regular star-polytopes Dimension 2)