واجاجاي
| واجاجاي Mount Elgon | |
|---|---|
| Wagagai (summit) | |
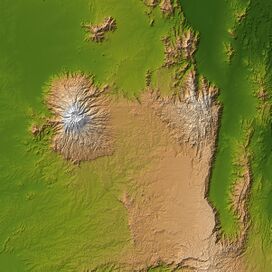 Mount Elgon (left) and Great Rift Valley (right) | |
| أعلى نقطة | |
| الارتفاع | 4،321 m (14،177 ft)[1] Ranked 17th in Africa |
| البروز | 2،458 m (8،064 ft)[1] |
| العزلة | 339 km (211 mi)[2] |
| الإدراج | Ultra |
| الإحداثيات | 01°07′06″N 34°31′30″E / 1.11833°N 34.52500°E[1] |
| الجغرافيا | |
| خطأ: الوظيفة "autocaption" غير موجودة. | |
| الخريطة الطبوغرافية | Mount Elgon Map and Guide[3] |
| الجيولوجيا | |
| عمر الصخر | أصل ميوسين |
| نوع الجبل | بركان درعي |
| آخر ثوران | مجهول |
| التسلق | |
| أول صعود | 1911 بواسطة كمونك وستيجلر |
| أسهل السبل | التدافع |
واجاجاي هو بركان درعي منقرض على حدود أوغندا وكينيا،[4] شمال كيسومو وغرب كيتالي. أعلى نقطة في الجبل، المسماة "واجاجاي"، تقع بالكامل داخل أوغندا.[1][5] على الرغم من عدم وجود دليل يمكن التحقق منه على أول نشاط بركاني له، يقدر الجيولوجيون أن جبل إلجون يبلغ من العمر 24 مليون سنة على الأقل، مما يجعله أقدم بركان خامد في شرق إفريقيا.[6]
خصائص فيزيائية
جبل إلجون هو جبل بركاني ضخم يقع على حدود شرق أوغندا وغرب كينيا. شكله الواسع، قطره 80 كيلو متر (50 ميل)، يرتفع 3.070 متر (10.070 قدم) فوق السهول المحيطة. توفر ارتفاعاتها الأكثر برودة فترة راحة للبشر من السهول الساخنة أدناه، وتوفر ارتفاعاتها المرتفعة ملاذاً للنباتات والحيوانات.
يتكون جبل إلجون من خمس قمم رئيسية:
- واجاجاي (4.321 متر (14.177 قدم))، في أوغندا
- سوديك (4.302 متر (14.114 قدم)) على الحدود بين كينيا وأوغندا
- كويتوبوس (4.222 متر (13.852 قدم))، عمود بازلت مسطح القمة في كينيا
- موبيي (4.211 متر (13.816 قدم)) في أوغندا
- مسابا (4.161 متر (13.652 قدم)) في أوغندا
Other features of note are:
- The caldera — Elgon's is one of the largest intact calderas in the world.[7]
- The warm springs by the Suam River[8]
- Endebess Bluff (2،563 متر (8،409 ft))[9]
- Ngwarisha, Makingeny, Chepnyalil, and Kitum caves: Kitum Cave is over 60 متر (200 ft) wide and penetrates 200 متر (660 ft). The cave contains salt deposits and it is frequented by wild elephants that lick the salt exposed by gouging the walls with their tusks.[10] It became notorious following the publication of Richard Preston's book The Hot Zone in 1994 for its association with the Marburg virus after two people who had visited the cave (one in 1980 and another in 1987) contracted the disease and died.[11]
The mountain soils are red laterite. The mountain is the catchment area for the several rivers such as the Suam River, which becomes the Turkwel downstream and drains into Lake Turkana, and the Nzoia River and the Lwakhakha River, which flow to Lake Victoria. The town of Kitale is in the foothills of the mountain. The area around the mountain is protected by two Mount Elgon National Parks, one on each side of the international border.
النباتية
تم العثور على بعض النباتات النادرة في الجبل، بما في ذلك Ardisiandra wettsteinii، Carduus afromontanus، Echinops hoehnelii، Ranunculus keniensis، وRomulea keniensis.[12]
الأعراق المحلية
يعد جبل إلجون وروافده موطنًا لأربع قبائل، باجيسو، و سابينجاك، و ساباوت، وأوجيك، المعروفين في المنطقة تحت مصطلح ندوروبو المهين.[13]
انظر أيضاً
- قائمة الأرقام القصوى في أفريقيا
- 2010 Ugandan landslide
- List of volcanoes in Kenya
- Elgon languages
- Mount Elgon insurgency
- Breast shaped hills
المصادر
- ^ أ ب ت ث Africa Ultra-Prominences Peaklist.org. Retrieved 2012-01-11.
- ^ [1] peakbagger.com, retrieved 19 March 2017
- ^ Mount Elgon Map and Guide (Map) (1st ed.). 1:50,000 with mountaineering information. EWP. 1989. ISBN 0-906227-46-1.
- ^ "Uganda Wildlife Authority". www.uwa.or.ug. Archived from the original on 2007-12-24. Retrieved 2008-03-16.
- ^ "Mount Elgon, Uganda" Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 11 January 2012
- ^ NASA (28 August 2005). "SRTM Africa Images". NASA. Retrieved 24 October 2015.
- ^ "Mount Elgon | Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center". eros.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2020-05-30.
- ^ techadmin. "Kenya Hikes Archives - Page 2 of 2". Dickson's Mountains Expeditions (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). Retrieved 2020-05-30.
- ^ "What you need to know about Mt. Elgon Park in Uganda -" (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). Retrieved 2020-05-30.
- ^ "Underground Elephants Resurface | Wild Kingdom | Animal Planet". Animal.discovery.com. 2012-05-15. Retrieved 2018-08-10.
- ^ Preston, Richard, The Hot Zone : The Terrifying True-Life Thriller, Bantam Books, 1994.
- ^ "SiteBuilder". www.tour-uganda.com.
- ^ Scott, Penny (1998). From Conflict to Collaboration: People and Forests at Mount Elgon, Uganda. IUCN. ISBN 2-8317-0385-9.
وصلات خارجية
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- CS1 الإنجليزية الأمريكية-language sources (en-us)
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Articles with dead external links from February 2018
- الحدود الأوغندية الكينية
- براكين الوادي المتصدع الكبير
- براكين خامدة
- براكين طبقية في أوغندا
- براكين طبقية في كينيا
- جبال أفريقيا الدولية
- جبال أوغندا
- جبال كينيا
- كالديرات أفريقيا