قائمة أنظمة العد
| أنظمة الأرقام حسب الثقافة | |
|---|---|
| الأرقام الهندية العربية | |
| العربية المغربية العربية المشرقية الخمير |
العائلة الهندية البراهمية التايلندية |
| أرقام شرق آسيا | |
| الصينية سوژو عصي العد |
اليابانية الكورية |
| الأرقام الأبجدية | |
| أبجد الأرمنية السيريلية جعيز |
العبرية اليونانية (Ionian) أريابهاتا |
| أنظمة أخرى | |
| Attic البابلية المصرية الإتروسكية |
المايا الرومانية Urnfield |
| قائمة مواضيع نظم الأرقام | |
| Positional systems by base | |
| عشري (10) | |
| 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 | |
| 1, 3, 9, 12, 20, 24, 30, 36, 60, more… | |
تتضمن هذه المقالة قائمة أنظة العد، وهي عبارة عن أنظمة الكتابة المسستخدم لتمثيل الأرقام.
حسب الثقافة
| الاسم | القاعدة | مثال | أول ظهور تقريبي | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| الأعداد البابلية | 60 | 3100 ق.م. | |||||||||||||||||
| الأعداد المصرية | 10 |
or
|
3000 ق.م. | ||||||||||||||||
| أعداد المايا | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||
| الأرقام الصينية، الأرقام اليابانية، الأرقام الكورية (الصينية-الكورية) | 10 | 零 一 二 三 四 五 六 七 八 九 | |||||||||||||||||
| الأعداد الرومانية | 10 | Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ Ⅵ Ⅶ Ⅷ Ⅸ Ⅹ | 1000 ق.م. | ||||||||||||||||
| الأرقام اليونانية | 10 | α β γ δ ε ϝ ζ η θ ι | بعد 100 ق.م. | ||||||||||||||||
| Chinese rod numerals | 10 | القرن الأول | |||||||||||||||||
| الأعداد الهندية العربية | 10 | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | القرن التاسع | ||||||||||||||||
| Location arithmetic لجون ناپيير | 2 | a b ab c ac bc abc d ad bd | 1617 في Rabdology, a non-positional binary system |
حسب نوع الترميز
أنظمة العد القياسية
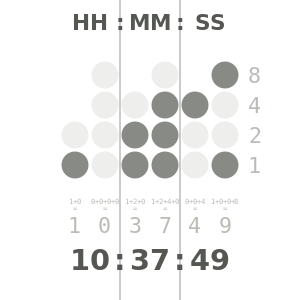
A binary clock might use LEDs to express binary values. In this clock, each column of LEDs shows a binary-coded decimal numeral of the traditional sexagesimal time.
| القاعدة | الاسم | الاستخدام |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | ثنائي | الحاسوب الرقمي |
| 3 | ثلاثي | Cantor set (all points in [0,1] that can be represented in ternary with no 1s); counting Tasbih in Islam; hand-foot-yard and teaspoon-tablespoon-shot measurement systems; most economical integer base |
| 4 | رباعي | Data transmission and Hilbert curves; Chumashan languages, and Kharosthi numerals |
| 5 | خماسي | Gumatj, Nunggubuyu, Kuurn Kopan Noot, and Saraveca languages; common count grouping e.g. tally marks |
| 6 | سداسي | Diceware, Ndom, Kanum, and Proto-Uralic language (suspected) |
| 8 | ثماني | Charles XII of Sweden, Unix-like permissions, DEC PDP-11, compact notation for binary numbers |
| 10 | عشري | Most widely used by modern civilizations[1][2][3] |
| 11 | Undecimal | Jokingly proposed during the French Revolution to settle a dispute between those proposing a shift to duodecimal and those who were content with decimal |
| 12 | نظام عد ثنائي عشر | Languages in the Nigerian Middle Belt Janji, Gbiri-Niragu, Piti, and the Nimbia dialect of Gwandara; Chepang language of Nepal, and the Mahl dialect of Maldivian; dozen-gross-great gross counting; hours and months timekeeping; years of Chinese zodiac; foot and inch. |
| 13 | نظام عد ثلاثي عشر | Conway base 13 function |
| 14 | نظام عد رباعي عشر | Programming for the HP 9100A/B calculator[4] and image processing applications[5] |
| 15 | Pentadecimal | Telephony routing over IP, and the Huli language |
| 16 | Hexadecimal | Base16 encoding; compact notation for binary data; tonal system |
| 20 | Vigesimal | Celtic, Maya, Inuit, Yoruba, Tlingit, and Dzongkha numerals; Santali, and Ainu languages |
| 24 | Tetravigesimal | Kaugel language |
| 27 | Heptavigesimal | Mapping the nonzero digits to the alphabet and zero to the space is occasionally used to provide checksums for alphabetic data such as personal names,[6] to provide a concise encoding of alphabetic strings,[7] or as the basis for a form of gematria.[8] |
| 30 | Trigesimal | The Natural Area Code |
| 32 | Duotrigesimal | Base32 encoding and the Ngiti language |
| 36 | Hexatrigesimal | Base36 encoding; use of letters with digits |
| 60 | Sexagesimal | Babylonian numerals; degrees-minutes-seconds and hours-minutes-seconds measurement systems; Ekari and Sumerian languages |
| 64 | Tetrasexagesimal | Base64 encoding |
| 85 | Pentoctogesimal | Ascii85 encoding |
أنظم العد الغير قياسية
Bijective numeration
| القاعدة | الاسم | الاستخدام |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Unary (Bijective base-1) | Tally marks |
| 10 | Bijective base-10 | |
| 26 | Bijective base-26 | Spreadsheet column numeration. Also used by John Nash as part of his obsession with numerology and the uncovering of "hidden" messages.[9] |
Signed-digit representation
| القاعدة | الاسم | الاستخدام |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Balanced binary (Non-adjacent form) | |
| 3 | Balanced ternary | Ternary computers |
| 10 | Balanced decimal | John Colson Augustin Cauchy |
القواعد السلبية
| القاعدة | الاسم | الاستخدام |
|---|---|---|
| −2 | Negabinary | |
| −3 | Negaternary | |
| −10 | Negadecimal |
القواعد المركبة
| القاعد | الاسم | الاستخدام |
|---|---|---|
| 2i | Quater-imaginary base | |
| −1 ± i | Twindragon base | Twindragon fractal shape |
القواعد الغير صحيحة
| القاعدة | الاسم | الاستخدام |
|---|---|---|
| φ | Golden ratio base | Early Beta encoder[10] |
| e | Base | Lowest radix economy |
| π | Base "Pi-nary" | |
| √2 | Base | |
| ¹²√2 | Base | Scientific pitch notation |
أخرى
الترميز الغير متوضع
انظر أيضاً
المصادر
- ^ The History of Arithmetic, Louis Charles Karpinski, 200pp, Rand McNally & Company, 1925.
- ^ Histoire universelle des chiffres, Georges Ifrah, Robert Laffont, 1994.
- ^ The Universal History of Numbers: From prehistory to the invention of the computer, Georges Ifrah, ISBN 0-471-39340-1, John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York, 2000. Translated from the French by David Bellos, E.F. Harding, Sophie Wood and Ian Monk
- ^ HP Museum
- ^ Free Patents Online
- ^ Grannis, Shaun J.; Overhage, J. Marc; McDonald, Clement J. (2002), "Analysis of identifier performance using a deterministic linkage algorithm", Proc AMIA Symp., pp. 305–309, PMID 12463836.
- ^ Stephens, Kenneth Rod (1996), Visual Basic Algorithms: A Developer's Sourcebook of Ready-to-run Code, Wiley, p. 215, ISBN 9780471134183.
- ^ Sallows, Lee (1993), "Base 27: the key to a new gematria", Word Ways 26 (2): 67–77, http://digitalcommons.butler.edu/wordways/vol26/iss2/2/.
- ^ Nasar, Sylvia (2001). A Beautiful Mind. Simon and Schuster. pp. 333–6. ISBN 0-7432-2457-4.
- ^ Ward, Rachel (2008), "On Robustness Properties of Beta Encoders and Golden Ratio Encoders", IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 54 (9): 4324–4334, doi:
All content in this article is created by Marefa contributors and is © Marefa. All rights reserved.



![{\displaystyle {\sqrt[{12}]{2}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bc835f27425fb3140e1f75a5faa35b1e8b9efc35)