لوراخ
Lörrach | |
|---|---|
 Aerial view at Lörrach from the north | |
| الإحداثيات: 47°37′N 7°40′E / 47.617°N 7.667°E | |
| البلد | ألمانيا |
| الولاية | بادن-ڤورتمبرگ |
| Admin. region | Freiburg |
| District | Lörrach |
| الحكومة | |
| • العمدة | Jörg Lutz |
| المساحة | |
| • الإجمالي | 39٫43 كم² (15٫22 ميل²) |
| المنسوب | 294 m (965 ft) |
| التعداد (31 ديسمبر 2006) | |
| • الإجمالي | 47٬707 |
| • الكثافة | 1٬200/km2 (3٬100/sq mi) |
| منطقة التوقيت | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 79501-79541 |
| Dialling codes | (+49) 07621 |
| لوحة السيارة | LÖ |
| الموقع الإلكتروني | loerrach.de |
Lörrach النطق الألماني: [ˈlœrax][2] is a city in southwest Germany, in the valley of the Wiese, close to the French and the Swiss borders. It is the capital of the district of Lörrach in Baden-Württemberg. It is the home of a number of large employers, including the Milka chocolate factory owned by Mondelez International. The city population has grown over the last century, with only 10,794 in 1905[citation needed] it has now increased its population to 49,382.[3]
Nearby is the castle of Rötteln on the Wiesental, whose lords became the counts of Hachberg and a residence of the Margraves of Baden; this was destroyed by the troops of Louis XIV in 1678, but was rebuilt in 1867. Lörrach received market rights in 1403, but it did not obtain the privileges of a city until 1682.
After the Napoleonic epoch, the town was included in the Grand Duchy of Baden. On September 21, 1848, Gustav Struve attempted to start a revolutionary uprising in Lörrach as part of the Revolutions of 1848-49. It failed, and Struve was caught and imprisoned. Still, Lörrach was officially the capital of Germany for a day.
الجغرافيا
Lörrach is located in the southernmost part of the Rhine Rift valley. The depression is created by tectonic movements, and the area has a high earthquake risk. Several times a year, Lörrach is afflicted by slight and medial earthquakes.
The city is located in a valley of the Quaternary period. Lörrach is surrounded by slopes on two sides. The slopes create the southern part of the Wiesental, that is the valley where the Wiese river flows.
Geographical locations of the subdistrict Lörrach:
- Elevation of the deepest place: 272 m (in the valley Wiesental at the border with Switzerland)
- Elevation of the highest place: 570 m (in the forest of Rötteln)
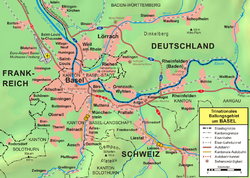
The extent of the urban area from south to north is 6.0 km and from east to west 4.6 km. Lörrach is also the capital city of Markgräflerland and a part of the tri-national agglomeration area of Basel. Stuttgart is 220 km away from Lörrach, and it takes one hour to drive to Bern or Zürich. The city has several forested hills along the valley Wiesental: Schädelberg, Homburg, Röttler Wald, and Tüllinger Berg.
Lörrach is bounded by many municipalities and the city of Basel. In addition, it is located in the foothills of the Black Forest and on the border of Switzerland.
| Binzen | Rümmingen | Steinen |
| Weil am Rhein | 
|
Rheinfelden |
| Basel | Riehen | Inzlingen Grenzach-Wyhlen |
Climate
Lörrach's climate is mild, and in the summer, it is often hot[مطلوب توضيح]. The region of Markgräflerland is the warmest in Germany because of the Mediterranean air current from the valley of the Rhône. Because of its numerous sunny days, the region is dubbed the German Tuscany (German: Die Toskana Deutschlands).
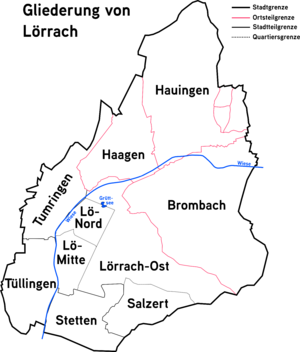
Boroughs and districts
Lörrach is subdivided into three boroughs and three districts. In sum, the three boroughs have an area of 18.6 km².
| Year of incorporation |
Boroughs and districts | Area (km²) |
|---|---|---|
| 1935 | Borough Tumringen | 4,4 |
| 1935 | Borough Tüllingen | 2,1 |
| 1908 | Borough Stetten | 4,6 |
| 1974 | District Haagen | 3.6 |
| 1975 | District Brombach | 9.8 |
| 1975 | District Hauingen | 7.4 |
The three districts have their own administrations with a chief magistrate (Ortsvorsteher). Every five years, the citizens of Lörrach elect the council of the districts. The satellite city Salzert was developed in 1963. Inzlingen, close to Lörrach, is an independent municipality, but Lörrach oversees its administration.
التاريخ
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1102 | Lörrach was first mentioned as the settlement Lorracho. |
| 1403 | Rupert of Germany declared Lörrach a market town. |
| 1678 | The castle of Rötteln was destroyed by the French. |
| 1682 | Lörrach was granted town privileges by Frederick VII, Margrave of Baden-Durlach. |
| 1702 | Battle of Käferholz against the French |
| 1756 | The town received a new civic law and its first town hall. |
| 1783 | Johann Peter Hebel became a teacher at the boarding school. |
| 1803 | Stetten became a part of Baden, having previously belonged to Austria. |
| 1808 | In Lörrach, numerous buildings in the classical style were built (synagogue, Stadtkirche, and Fridolinskirche) |
| 1835 | The state Baden joins the Zollverein. |
| 1848 | In September, Gustav Struve declared the new 'German Republic' from the town hall of Lörrach after the failed revolution. Some days later, he was arrested. |
| 1862 | The Wiesentalbahn between Basel, Lörrach, and Schopfheim was opened. A railway connection to Weil and Säckingen was extended to Lörrach in 1890. Also, Carl Christian Renaux was born on 11 March. |
| 1863 | Lörrach became a district town. |
| 1871 | The first elementary school was opened. |
| 1880 | Philippe Suchard created a chocolate factory in Lörrach. |
| 1908 | Incorporation of Stetten; later, Tüllingen und Tumringen (1935), Haagen (voluntary 1974), Brombach und Hauingen (1975), were incorporated. |
| 1945 | Air raid on Brombach and Lörrach: On April 24, French troops occupied the city. |
| 1963 | Start of construction of the district of Salzert |
| 1983 | The fourth Landesgartenschau of Baden-Wuerttemberg (a national horticultural show) was held in the new park area in the Grütt. |
| 1984 | The finished motorway section between High Rhine and Upper Rhine relieved the heavy traffic of the city. |
| 1991 | Inauguration of the new pedestrian precinct and the transformation of the city centre |
| 2010 | Two were killed and one injured in a shooting incident at the Saint Elizabeth Hospital.[4] |
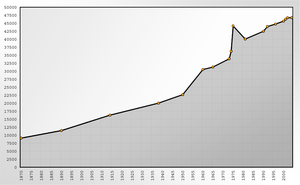
Population development
| Year | Population | Year | Population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1870 | 9,103 | 1975 | 44,179 | |
| 1890 | 11,475 | 1981 | 40,064 | |
| 1914 | 16,293 | 1990 | 42,500 | |
| 1938 | 20,041 | 1992 | 43,976 | |
| 1950 | 22,698 | 1996 | 44,756 | |
| 1960 | 30,546 | 2000 | 45,679 | |
| 1965 | 31,324 | 2001 | 46,272 | |
| 1973 | 33,885 | 2002 | 46,741 | |
| 1974 | 36,231 | 2004 | 46,754 |
source: Statistisches Landesamt Stuttgart, Statistischer Jahresbericht der Stadt Lörrach.[5]
Coat of arms


Twin towns - sister cities
Lörrach is twinned with:[6]
 Sens, France, since 1966
Sens, France, since 1966 Senigallia, Italy, since 1986
Senigallia, Italy, since 1986 Village-Neuf, France, since 1988
Village-Neuf, France, since 1988 Meerane, Germany, since 1990
Meerane, Germany, since 1990 Chester, United Kingdom, since 2002
Chester, United Kingdom, since 2002
See also
Sources
- ^ "Annual area and population data for Lörrach". Statistisches Landesamt Baden-Württemburg (in German). Archived from the original on 2013-07-23. Retrieved 2008-01-21.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ Duden Das Aussprachewörterbuch (6 ed.). Dudenverlag. p. 518. ISBN 978-3-411-04066-7.
- ^ (in German)Bevölkerung nach Nationalität – vierteljährlich, Statistisches Landesamt Baden-Württemberg, 2020, https://www.statistik-bw.de/BevoelkGebiet/Bevoelkerung/01035055.tab?R=GS336050, retrieved on 2020-05-16
- ^ "Fatal shooting at German hospital". BBC News. 19 September 2010.
- ^ "Population development from Statistischen Landesamt Stuttgart". Statistik-bw.de. 2011-07-29. Archived from the original on 2008-03-05. Retrieved 2012-01-15.
- ^ "Partnerstädte & Städtefreundschaften". loerrach.de (in الألمانية). Lörrach. Retrieved 2019-11-27.
External links
- Official website (German)
- (in ألمانية) Lörrach:History and images
- Lörrach Civic Heraldry
- Daily Newspaper of the area
- Daily Newspaper of the area
- News and musings from Weil am Rhein - German town near Loerrach on the Basle border triangle
- Burg Rötteln: Picture Gallery
- Burghof Cultural Event Centre and Theatre
- Cultural Youth events in Loerrach
- 'Stimmen' Loerrach
- 'Metal Forces Festival' Loerrach
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- CS1 الألمانية-language sources (de)
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Germany articles requiring maintenance
- Pages using infobox German location with unknown parameters
- Towns in Baden-Württemberg
- Articles with unsourced statements from May 2020
- جميع الصفحات التي تحتاج تنظيف
- مقالات بالمعرفة تحتاج توضيح from September 2010
- Articles with ألمانية-language sources (de)
- Lörrach (district)
- Germany–Switzerland border crossings
- بادن