بروميد الألومنيوم
| |

| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك المفضل
Aluminium bromide | |
| أسماء أخرى
aluminium(III) bromide
aluminium tribromide | |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.891 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| رقم RTECS |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | AlBr3 Al2Br6 |
| كتلة مولية | 266.69 g/mol |
| المظهر | white to pale yellow crystalline solid |
| الكثافة | 3.205 g/cm3 |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| نقطة الغليان | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | reacts |
| قابلية الذوبان | slightly soluble in methanol, diethyl ether, acetone |
| المخاطر | |
تبويب الاتحاد الاوروپي (DSD)
|
not listed |
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |
| الجرعة أو التركيز القاتل (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (الجرعة الوسطى)
|
1598 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |
أنيونات أخرى
|
ثلاثي كلوريد الألومنيوم يوديد الألومنيوم |
كاتيونات أخرى
|
ثلاثي بروميد البورون |
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
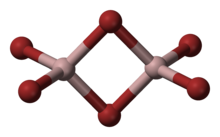
بروميد الألمنيوم مركب كيميائي له الصيغة AlBr3 ، ويكون على شكل بلورات بيضاء إلى صفراء شاحبة .
الخواص
- يوجد في الحالة الصلبة على شكل Al2Br6 حيث تشكل أيوني بروميد جسرا بين مركزي الألومنيوم بالتالي يحقق الألومنيوم قاعدة الثمانيات.
- مركب بروميد الألومنيوم حساس للرطوبة، حيث تصدر منه أبخرة عند التماس مع الهواء الرطب.
- يتفاعل بعنف مع الماء البارد ويتفكك في الماء الساخن، لكنه ينحل في أغلب المحلات العضوية مثل الأسيتون واالهكسان.
- يتفكك مركب بروميد الألومنيوم بالتسخين إلى الفلزات المكونة البروم والألومنيوم.
- 2AlBr3 –Δ→ 2Al + 3Br2
التفاعلات الكيميائية
يتفاعل مع رباعي كلورو الميثان عند الدرجة 100°س ليعطي رباعي برومو الميثان حسب المعادلة
- 4 AlBr3 + 3 CCl4 → 4 AlCl3 + 3 CBr4
يتفاعل مع غاز الفوسجين حيث يعطي بروميد الكربونيل وكلوروبروميد الألومنيوم
- AlBr3 + COCl2 → COBr2 + AlCl2Br
التحضير
By far the most common form of aluminium bromide is Al2Br6. This species exists as hygroscopic colorless solid at standard conditions. Typical impure samples are yellowish or even red-brown due to the presence of iron-containing impurities. يحضر مركب بروميد الألومنيوم من تفاعل البروم مع الألومنيوم:
- 2 Al + 6 HBr → Al2Br6 + 3 H2
Alternatively, the direct bromination occurs also:
- 2 Al + 3 Br2 → Al2Br6
التفاعلات
Al2Br6 dissociates readily to give the strong Lewis acid, AlBr3. Regarding the tendency of Al2Br6 to dimerize, it is common for heavier main group halides to exist as aggregates larger than implied by their empirical formulae. Lighter main group halides such as boron tribromide do not show this tendency, in part due to the smaller size of the central atom.
Consistent with its Lewis acidic character, Al2Br6 is hydrolyzed by water with evolution of HBr and formation of Al-OH-Br species. Similarly, it also reacts quickly with alcohols and carboxylic acids, although less vigorously than with water. With simple Lewis bases (L), Al2Br6 forms adducts, such as AlBr3L.
Aluminium tribromide reacts with رابع كلوريد الكربون at 100 °C to form رابع بروميد الكربون:
- 4 AlBr3 + 3 CCl4 → 4 AlCl3 + 3 CBr4
and with phosgene yields بروميد الكربونيل and كلوروبروميد الألومنيوم:[citation needed]
- AlBr3 + COCl2 → COBr2 + AlCl2Br
Al2Br6 is used as a catalyst for the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction.[1] Related Lewis acid-promoted reactions include as epoxide ring openings and decomplexation of dienes from iron carbonyls. It is a stronger Lewis acid than the more common Al2Cl6.
الاستخدامات
- يستخدم مركب بروميد الأومنيوم كحفاز في العديد من تفاعلات الكيمياء العضوية مثل تفاعل ألكلة فريدل-كرافتس وبعض تفاعلات البلمرة.
المصادر
- Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ^ Paquette, Leo A. (2001). Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X. hdl:10261/236866. ISBN 0471936235.
- Pages using Chembox with unknown parameters
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Chembox
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles with unsourced statements from May 2010
- بروميدات
- مركبات الألومنيوم
- هاليدات فلزية
