دوديكان
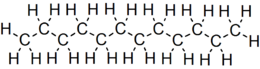
| |
| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك المفضل
Dodecane[1] | |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| مرجع بايلستاين | 1697175 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.607 |
| رقم EC |
|
| مرجع Gmelin | 201408 |
| KEGG | |
| عناوين مواضيع طبية MeSH | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| رقم RTECS |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | C12H26 |
| كتلة مولية | 170.33 g mol-1 |
| المظهر | Colorless liquid |
| الرائحة | Gasoline-like to odorless |
| الكثافة | 0.7495 g mL−1 at 20 °C[2] |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| نقطة الغليان | |
| log P | 6.821 |
| ضغط البخار | 18 Pa (at 25 °C)[3] |
| kH | 1.4 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| معامل الانكسار (nD) | 1.421 |
| اللزوجة | 1.34 mPa s |
| الكيمياء الحرارية | |
| الإنتالپية المعيارية للتشكل ΔfH |
−353.5–−350.7 kJ mol−1 |
| الانتالبية المعيارية للاحتراق ΔcH |
−7901.74 kJ mol−1 |
| Standard molar entropy S |
490.66 J K−1 mol−1 |
| سعة الحرارة النوعية، C | 376.00 J K−1 mol−1 |
| المخاطر | |
| صفحة بيانات السلامة | hazard.com |
| ن.م.ع. مخطط تصويري | 
|
| ن.م.ع. كلمة الاشارة | DANGER |
| H304 | |
| P301+P310, P331 | |
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |
| نقطة الوميض | 71 °C (160 °F; 344 K) |
| 205 °C (401 °F; 478 K) | |
| حدود الانفجار | 0.6% |
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |
alkanes ذات العلاقة
|
|
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
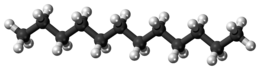
الدوديكان (يعرف أيضا ثنائي هيكسيل, أداكان 12) هو أحد الألكانات الهيدروكربونية, وله الصيغة البنائية CH3(CH2)10CH3, وهو مادة زيتية سميكة من سلسلة البرافينات.
ويستخدم كمذيب و distillation chaser, and scintillator component. It is used as a diluent for tributyl phosphate (TBP) in nuclear reprocessing plants.[4]
تفاعل الاشتعال
The combustion reaction of dodecane is as follows:
- C12H26(l) + 18.5 O2(g) → 12 CO2(g) + 13 H2O(g)
One litre of fuel needs about 15 kg of air to burn (2.6 kg of oxygen), and generates 2.3 kg (or 1.2 m3) of CO2 upon complete combustion.
Jet fuel surrogate
In recent years, n-dodecane has garnered attention as a possible surrogate for kerosene-based fuels such as Jet-A, S-8, and other conventional aviation fuels. It is considered a second-generation fuel surrogate designed to emulate the laminar flame speed, largely supplanting n-decane, primarily due to its higher molecular mass and lower hydrogen-to-carbon ratio which better reflect the n-alkane content of jet fuels.
انظر أيضاً
المراجع
- Caudwell, D.R. (2003-06-16). "The Viscosity and Density of n-Dodecane and n-Octadecane at Pressures up to 200 mPa and Temperatures up to 473 K" (pdf). NIST. Retrieved 2007-10-09.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
وصلات خارجية
المصادر
- ويكيبيديا الإنجليزية.
- ^ "n-dodecane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ "Dodecane".
- ^ "Dodecane".
- ^ Rydberg, Jan (2004). Solvent Extraction Principles and Practice. Marcel Dekker. p. 524. ISBN 0-8247-5063-2.
