الهندو-إيرانيون
| جزء من سلسلة عن |
| المواضيع الهندو-أوروپية |
|---|
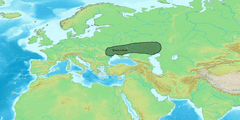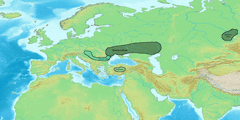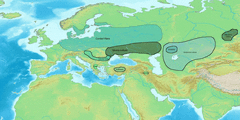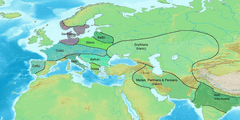 |
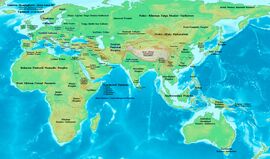
الشعوب الهندو-إيرانية Indo-Iranian أو Indo-Iranic،[1] وأحياناً بإسم آريا Arya أو الآريون من تعريفهم الذاتي، كانوا جماعة لغوية عرقية جلبوا اللغات الهندو-إيرانية، التي كانت فرعاً رئيسياً من عائلة اللغات الهندو-أوروپية، إلى أجزاء رئيسية في أوراسيا.
المسميات
The term Aryan has long been used to denote the Indo-Iranians, because Arya was the self-designation of the ancient speakers of the Indo-Iranian languages, specifically the Iranian and the Indo-Aryan peoples, collectively known as the Indo-Iranians.[2][3] Despite this, some scholars use the term Indo-Iranian to refer to this group, though the term "Aryan" remains widely used by most scholars, such as Josef Wiesehofer,[4] Will Durant,[5] and Jaakko Häkkinen.[6][7] Population geneticist Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza, in his 1994 book The History and Geography of Human Genes, also uses the term Aryan to describe the Indo-Iranians.[8]
التاريخ
الأصل
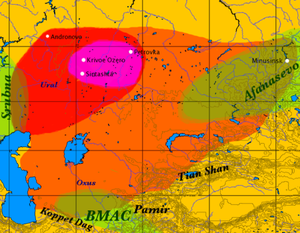
The early Indo-Iranians are commonly identified with the descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans known as the Sintashta culture and the subsequent Andronovo culture within the broader Andronovo horizon, and their homeland with an area of the Eurasian steppe that borders the Ural River on the west, the Tian Shan on the east (where the Indo-Iranians took over the area occupied by the earlier Afanasevo culture), and Transoxiana and the Hindu Kush on the south.[9]
Based on its use by Indo-Aryans in Mitanni and Vedic India, its prior absence in the Near East and Harappan India, and its 19th–20th century BC attestation at the Andronovo site of Sintashta, Kuzmina (1994) argues that the chariot corroborates the identification of Andronovo as Indo-Iranian.[note 1] Anthony & Vinogradov (1995) dated a chariot burial at Krivoye Lake to about 2000 BC, and a Bactria-Margiana burial that also contains a foal has recently been found, indicating further links with the steppes.[13]
Historical linguists broadly estimate that a continuum of Indo-Iranian languages probably began to diverge by 2000 BC,[14] preceding both the Vedic and Iranian cultures which emerged later. The earliest recorded forms of these languages, Vedic Sanskrit and Gathic Avestan, are remarkably similar, descended from the common Proto-Indo-Iranian language. The origin and earliest relationship between the Nuristani languages and that of the Iranian and Indo-Aryan groups is not completely clear.
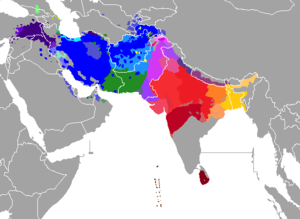
التوسع


الموجة الأولى – الهندو-آريون
Two-wave models of Indo-Iranian expansion have been proposed by Burrow (1973)[17] and Parpola (1999). The Indo-Iranians and their expansion are strongly associated with the Proto-Indo-European invention of the chariot. It is assumed that this expansion spread from the Proto-Indo-European homeland north of the Caspian Sea south إلى القوقاز وآسيا الوسطى، والهضبة الإيرانية وشبه القارة الهندية.
ميتاني الأناضول
الميتانـّي، وهم شعب يُعرف في شرق الأناضول منذ حوالي 1500 ق.م.، كان من أصول مختلطة: An indigenous non Indo-European Hurrian-speaking majority was supposedly dominated by a non-Anatolian, Indo-Aryan elite.[18] There is linguistic evidence for such a superstrate, in the form of:
- a horse training manual written by a Mitanni man named Kikkuli, which was used by the Hittites, an Indo-European Anatolian people who spoke a non Indo-Iranian language;
- the names of Mitanni rulers and;
- the names of gods invoked by these rulers in treaties.
In particular, Kikkuli's text includes words such as aika "one" (i.e. a cognate of the Indo-Aryan eka), tera "three" (tri), panza "five" (pancha), satta "seven", (sapta), na "nine" (nava), and vartana "turn around", in the context of a horse race (Indo-Aryan vartana). In a treaty between the Hittites and the Mitanni, the Ashvin deities Mitra, Varuna, Indra, and Nasatya are invoked. These loanwords tend to connect the Mitanni superstrate to Indo-Aryan rather than Iranian languages – i.e. the early Iranian word for "one" was aiva.[بحاجة لمصدر]
شبه القارة الهندية – الثقافة الڤيدية
The standard model for the entry of the Indo-European languages into the Indian subcontinent is that this first wave went over the Hindu Kush, either into the headwaters of the Indus and later the Ganges. The earliest stratum of Vedic Sanskrit, preserved only in the Rigveda, is assigned to roughly 1500 BC.[18][19] From the Indus, the Indo-Aryan languages spread from c. 1500 BC to c. 500 BC, over the northern and central parts of the subcontinent, sparing the extreme south. The Indo-Aryans in these areas established several powerful kingdoms and principalities in the region, from south eastern Afghanistan to the doorstep of Bengal. The most powerful of these kingdoms were the post-Rigvedic Kuru (in Kurukshetra and the Delhi area) and their allies the Pañcālas further east, as well as Gandhara and later on, about the time of the Buddha, the kingdom of Kosala and the quickly expanding realm of Magadha. The latter lasted until the 4th century BC, when it was conquered by Chandragupta Maurya and formed the center of the Mauryan empire.
In eastern Afghanistan and southwestern Pakistan, whatever Indo-Aryan languages were spoken there were eventually pushed out by the Iranian languages. Most Indo-Aryan languages, however, were and still are prominent in the rest of the Indian subcontinent. Today, Indo-Aryan languages are spoken in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Fiji, Suriname and the Maldives.
الموجة الثانية – الإيرانيون
The second wave is interpreted as the Iranian wave.[14]
The first Iranians to reach the Black Sea 'may' have been the Cimmerians in the 8th century BC, although their linguistic affiliation to Iranians is uncertain. They were followed by the Scythians, who are considered a western branch of the Central Asian Sakas. Sarmatian tribes, of whom the best known are the Roxolani (Rhoxolani), Iazyges (Jazyges) and the Alani (Alans), followed the Scythians westwards into Europe in the late centuries BC and the 1st and 2nd centuries AD (The Age of Migrations). The populous Sarmatian tribe of the Massagetae, dwelling near the Caspian Sea, were known to the early rulers of Persia in the Achaemenid Period. At their greatest reported extent, around 1st century AD, the Sarmatian tribes ranged from the Vistula River to the mouth of the Danube and eastward to the Volga, bordering the shores of the Black and Caspian seas as well as the Caucasus to the south.[note 2] In the east, the Saka occupied several areas in Xinjiang, from Khotan to Tumshuq.
The Medians, Persians and Parthians begin to appear on the Iranian plateau from ح. 800 BC, and the Achaemenids replaced the language isolate speaking Elamites rule over the region from 559 BC, although the Iranic peoples were largely subject to the Semitic speaking Assyrian Empire until the 6th century BC. Around the first millennium AD, Iranian groups began to settle on the eastern edge of the Iranian plateau, on the mountainous frontier of northwestern and western Pakistan, displacing the earlier Indo-Aryans from the area.
In Eastern Europe, the Iranians were eventually decisively assimilated (e.g. Slavicisation) and absorbed by the Proto-Slavic population of the region,[20][21][22][23] while in Central Asia, the Turkic languages marginalized the Iranian languages as a result of the Turkic expansion of the early centuries AD. Extant major Iranian languages are Persian, Pashto, Kurdish, and Balochi besides numerous smaller ones. Ossetian, primarily spoken in North Ossetia and South Ossetia, is a direct descendant of Alanic, and by that the only surviving Sarmatian language of the once wide-ranging East Iranian dialect continuum that stretched from Eastern Europe to the eastern parts of Central Asia.
الآثار
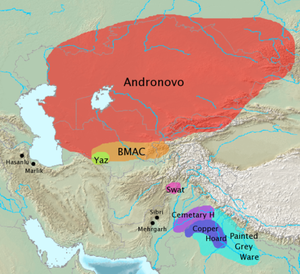
الثقافات الأثرية المقترنة بالتوسع الهند-إيراني تضم:
- أوروپا
- ثقافة پولتاڤا (2700–2100 ق.م.)
- آسيا الوسطى
- أفق أندرونوڤو (2200–1000 ق.م.)
- Sintashta-Petrovka-Arkaim (2200–1600 BC)
- Alakul (2100–1400 BC)
- Fedorovo (1400–1200 BC)
- Alekseyevka (1200–1000 BC)
- Bactria-Margiana Archaeological Complex (2200–1700 BC)
- Srubna culture (2000–1100 BC)
- Abashevo culture (1700–1500 BC)
- Yaz culture (1500–1100 BC)
- أفق أندرونوڤو (2200–1000 ق.م.)
- الهند (سهول الگنج الأوسط)
- Painted Gray Ware culture (1100–350 BC)
- Iran
- Early West Iranian Grey Ware (1500–1000 BC)
- Late West Iranian Buff Ware (900–700 BC)
- شبه القارة الهندية
- ثقافة سوات (1600–500 BC)
- Cemetery H culture (1900–1300 BC)
Parpola (1999) يقترح التمييزات التالية:
| النطاق الزمني | الثقافة الأثرية | التمييز المقترح من پارپولا |
|---|---|---|
| 2800–2000 BC | late Catacomb and Poltavka cultures | late PIE to Proto–Indo-Iranian |
| 2000–1800 BC | Srubna and Abashevo cultures | إيرانية-أولية |
| 2000–1800 BC | Petrovka-Sintashta | Proto–Indo-Aryan |
| 1900–1700 BC | BMAC | "Proto-Dasa" Indo-Aryans establishing themselves in the existing BMAC settlements, defeated by "Proto-Rigvedic" Indo-Aryans around 1700 |
| 1900–1400 BC | Cemetery H | داسا الهندية |
| 1800–1000 BC | Alakul-Fedorovo | Indo-Aryan, including "Proto–Sauma-Aryan" practicing the Soma cult |
| 1700–1400 BC | ثقافة سوات المبكرة | Proto-Rigvedic = Proto-Dardic |
| 1700–1500 BC | late BMAC | "Proto–Sauma-Dasa", assimilation of Proto-Dasa and Proto–Sauma-Aryan |
| 1500–1000 BC | Early West Iranian Grey Ware | Mitanni-Aryan (offshoot of "Proto–Sauma-Dasa") |
| 1400–800 BC | late Swat culture and Punjab, Painted Grey Ware | late Rigvedic |
| 1400–1100 BC | Yaz II-III, Seistan | Proto-Avestan |
| 1100–1000 BC | Gurgan Buff Ware, Late West Iranian Buff Ware | Proto-Persian, Proto-Median |
| 1000–400 BC | Iron Age cultures of Xinjang | ساكا-الأولية |
اللغة
The Indo-European language spoken by the Indo-Iranians in the late 3rd millennium BC was a Satem language still not removed very far from the Proto-Indo-European language, and in turn only removed by a few centuries from Vedic Sanskrit of the Rigveda. The main phonological change separating Proto–Indo-Iranian from Proto–Indo-European is the collapse of the ablauting vowels *e, *o, *a into a single vowel, Proto–Indo-Iranian *a (but see Brugmann's law). Grassmann's law and Bartholomae's law were also complete in Proto–Indo-Iranian, as well as the loss of the labiovelars (kw, etc.) to k, and the Eastern Indo-European (Satem) shift from palatized k' to ć, as in Proto–Indo-European *k'ṃto- > Indo-Iran. *ćata- > Sanskrit śata-, Old Iran. sata "100".
بين تغير الأصوات من الهندو-إيرانية-الأولية إلى الهندو-آرية نجد فقدان the voiced sibilant *z, بين أولئك إلى الإيرانية نجد the de-aspiration of the PIE voiced aspirates.
الدين
Despite the introduction of later Vedic and Zoroastrian scriptures, Indo-Iranians shared a common inheritance of concepts including the universal force *Hṛta- (Sanskrit rta, Avestan asha), the sacred plant and drink *sawHma- (Sanskrit Soma, Avestan Haoma) and gods of social order such as *mitra- (Sanskrit Mitra, Avestan and Old Persian Mithra, Miθra) and *bʰaga- (Sanskrit Bhaga, Avestan and Old Persian Baga). Proto-Indo-Iranian religion is an archaic offshoot of Indo-European religion. From the various and dispersed Indo-Iranian cultures, a set of common ideas may be reconstructed from which a common, unattested proto-Indo-Iranian source may be deduced.[24]
The pre-Islamic religion of the Nuristani people and extant religion of the Kalash people is significantly influenced by the original religion of the Indo-Iranians, infused with accretions developed locally.[25][26][27][28][29] Michael Witzel theorises that these religions might share some elements with Shinto, one of the national religions of Japan, which according to him may contain some Indo-Iranian influence owing to contact presumably in the steppes of Central Asia at around 2000 BC. In Shinto, traces of these can be seen in the myth of the storm god Susanoo slaying a serpent Yamata-no-Orochi and in the myth of the dawn goddess Ame-no-Uzume.[30][31][32]
معظم الهندو-آريين، اليوم، يتبعون ديانات إبراهيمية ودارمية.
التطور
Some beliefs developed in different ways as cultures separated and evolved. For example, the word 'daeva,' which appears in the Avesta, also bears a linguistic relationship to the Sanskrit word 'deva,' referring to one of the principal classes of gods, as well as other related words throughout the Indo-European traditions. Indeed, Indra, the greatest of the devas from Vedic literature, is often listed in Zoroastrian texts as one of the greatest of the evil forces, sometimes second only to Angra Mainyu himself.[33] In the traditional Zoroastrian confession of faith as recorded in the Avesta, the rejection of the daevas is one of the most significant qualifiers for a follower of the tradition, alongside worshipping Ahura Mazda and following the teachings of Zarathustra. Similarly, the parallels between the malevolent Vedic Asuras and benevolent Zoroastrian Ahuras are particularly obvious and striking.Varuna, the most powerful of the Asuras, does not directly correspond to Ahura Mazda but shares several traits in common with him, particularly in terms of his role as king among the lesser gods and arbiter of law and morality among mortals. Even as Ahura Mazda rules by and upholds asha, the cosmic moral order, in the Avesta, so too do Varuna and the Asuras uphold the analogous concept of rta in the Vedas.[33]
The Rig-Vedic Sarasvati is linguistically and functionally cognate with Avestan *Haraxvaitī Ārəduuī Sūrā Anāhitā.[بحاجة لمصدر] Both are described as world rivers. Vedic Saraswati is described as "Best of Mothers, Best of Rivers, Best of Goddesses".[34] Similarly, in early portions of the Avesta, Iranian *Harahvati is the world-river that flows down from the mythical central Mount Hara. She is blocked by an obstacle (Avestan for obstacle: vərəθra) placed there by Angra Mainyu.[24]
المصطلحات المشابهة
The following is a list of cognate terms that may be gleaned from comparative linguistic analysis of the Rigveda and Avesta. Both collections are from the period after the proposed date of separation (c. 2nd millennium BC) of the Proto-Indo-Iranians into their respective Indic and Iranian branches.[24][35][36]
| Vedic Sanskrit | Avestan | Common meaning |
|---|---|---|
| āp | āp | "water," āpas "the Waters"[36] |
| Apam Napat, Apām Napāt | Apām Napāt | the "water's offspring"[36] |
| aryaman | airyaman | "Arya-hood" (lit:** "member of Arya community")[36] |
| Asura Mahata/Medha (असुर महत/मेधा) | Ahura Mazda | "The Supreme Lord, Lord of Wisdom"[37][38] |
| rta | asha/arta | "active truth", extending to "order" and "righteousness"[36][35] |
| atharvan | āθrauuan, aθaurun Atar | "priest"[35] |
| ahi | azhi, (aži) | "dragon, snake", "serpent"[36] |
| daiva, deva | daeva, (daēuua) | a class of divinities |
| manu | manu | "man"[36] |
| mitra | mithra, miθra | "oath, covenant"[36][35] |
| asura | ahura | another class of spirits[36][35] |
| sarvatat | Hauruuatāt | "intactness", "perfection"[39][40] |
| Sarasvatī (Ārdrāvī śūrā anāhitā, आर्द्रावी शूरा अनाहिता) | Haraxvati/Haraxvaitī (Ārəduuī Sūrā Anāhitā) | a controversial (generally considered mythological) river, a river goddess[41][42] |
| sauma, soma | haoma | a plant, deified[36][35] |
| svar | hvar, xvar | the Sun, also cognate to Greek helios, Latin sol, Engl. Sun[39] |
| Tapati | tapaiti | Possible fire/solar goddess; see Tabiti (a possibly Hellenised Scythian theonym). Cognate with Latin tepeo and several other terms.[39] |
| Vrtra-/Vr̥tragʰná/Vritraban | verethra, vərəθra (cf. Verethragna, Vərəθraγna) | "obstacle"[36][35] |
| ياما | Yima | son of the solar deity Vivasvant/Vīuuahuuant[36] |
| yajña | yasna, object: yazata | "worship, sacrifice, oblation"[36][35] |
| Gandharva | Gandarewa | "heavenly beings"[36] |
| ناساتيا | Nanghaithya | "twin Vedic gods associated with the dawn, medicine, and sciences"[36] |
| Amarattya | Ameretat | "immortality"[36] |
| Póṣa | Apaosha | "demon of drought"[36] |
| Ashman | Asman | "sky, highest heaven"[39] |
| Angira Manyu | Angra Mainyu | "destructive/evil spirit, spirit, temper, ardour, passion, anger, teacher of divine knowledge"[36] |
| مانيا | Maniyu | "anger, wrath"[36] |
| Sarva | Sarva | "Rudra, Vedic god of wind, Shiva"[39] |
| Madhu | Madu | "honey"[36] |
| Bhuta | Buiti | "ghost"[36] |
| مانترا | Manthra | "sacred spell"[36] |
| Aramati | Armaiti | "piety" |
| Amrita | Amesha | "nectar of immortality"[36] |
| Amrita Spanda (अमृत स्पन्द) | Amesha Spenta | "holy nectar of immortality" |
| Sumati | Humata | "good thought"[39][36] |
| Sukta | Hukhta | "good word"[36] |
| Narasamsa | Nairyosangha | "praised man"[36] |
| Vayu | Vaiiu | "wind"[36] |
| Vajra | Vazra | "bolt"[36] |
| Ushas | Ushah | "dawn"[36] |
| Ahuti | azuiti | "offering"[36] |
| púraṁdhi | purendi[36] | |
| bhaga | baga | "lord, patron, wealth, prosperity, sharer/distributor of good fortune"[36] |
| Usij | Usij | "priest"[36] |
| تريتا | thrita | "the third"[36] |
| Mas | Mah | "moon, month"[36] |
| Vivasvant | Vivanhvant | "lighting up, matutinal"[36] |
| Druh | Druj | "Evil spirit"[36] |
| Ahi Dasaka | Azhi Dahaka | "biting serpent"[43] |
الجينات
R1a1a (R-M17 or R-M198) is the sub-clade most commonly associated with Indo-European speakers. Most discussions purportedly of R1a origins are actually about the origins of the dominant R1a1a (R-M17 or R-M198) sub-clade. Data so far collected indicates that there are two widely separated areas of high frequency, one in the Indian subcontinent, around North India, and the other in Eastern Europe, around Poland and Ukraine.[بحاجة لمصدر] The historical and prehistoric possible reasons for this are the subject of on-going discussion and attention amongst population geneticists and genetic genealogists, and are considered to be of potential interest to linguists and archaeologists also.
Out of 10 human male remains assigned to the Andronovo horizon from the Krasnoyarsk region, 9 possessed the R1a Y-chromosome haplogroup and one C-M130 haplogroup (xC3). mtDNA haplogroups of nine individuals assigned to the same Andronovo horizon and region were as follows: U4 (2 individuals), U2e, U5a1, Z, T1, T4, H, and K2b.
A 2004 study also established that during the Bronze Age/Iron Age period, the majority of the population of Kazakhstan (part of the Andronovo culture during Bronze Age), was of west Eurasian origin (with mtDNA haplogroups such as U, H, HV, T, I and W), and that prior to the 13th–7th century BC, all Kazakh samples belonged to European lineages.[44]
انظر أيضاً
ملاحظات
- ^ Klejn (1974), as cited in Bryant 2001:206, acknowledges the Iranian identification of the Andronovo culture, but finds the Andronovo culture too late[مطلوب توضيح] for an Indo-Iranian identification, giving a later date for the start of the Andronovo culture "in the 16th or 17th century BC, whereas the Aryans appeared in the Near East not later than the 15th to 16th century BC.[10] Klejn (1974, p.58) further argues that "these [latter] regions contain nothing reminiscent of Timber-Frame Andronovo materials."[10] Brentjes (1981) also gives a later dating for the Andronovo culture.[11] Bryant further refers to Lyonnet (1993) and Francfort (1989), who point to the absence of archaeological remains of the Andronovans south of the Hindu Kush.[11] Bosch-Gimpera (1973) and Hiebert (1998) argue that there also no Andronovo remains in Iran,[11] but Hiebert "agrees that the expansion of the BMAC people to the Iranian plateau and the Indus Valley borderlands at the beginning of the second millennium BC is 'the best candidate for an archaeological correlate of the introduction of Indo-Iranian speakers to Iran and South Asia' (Hiebert 1995:192)".[12] Sarianidi states that the Andronovo tribes "penetrated to a minimum extent".[11]
- ^ Apollonius (Argonautica, iii) envisaged the Sauromatai as the bitter foe of King Aietes of Colchis (modern Georgia).
الهامش
- ^ Naseer Dashti (8 October 2012). The Baloch and Balochistan: A historical account from the Beginning to the fall of the Baloch State. Trafford Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4669-5897-5.
- ^ The "Aryan" Language, Gherardo Gnoli, Instituto Italiano per l'Africa e l'Oriente, Roma, 2002.
- ^ . Schmitt, "Aryans" in Encyclopedia Iranica: Excerpt:"The name "Aryan" (OInd. ā́rya-, Ir. *arya- [with short a-], in Old Pers. ariya-, Av. airiia-, etc.) is the self-designation of the peoples of Ancient India and Ancient Iran who spoke Aryan languages, in contrast to the "non-Aryan" peoples of those "Aryan" countries (cf. OInd. an-ā́rya-, Av. an-airiia-, etc.), and lives on in ethnic names like Alan (Lat. Alani, NPers. īrān, Oss. Ir and Iron.". Also accessed online: [1] in May, 2010
- ^ Wiesehofer, Joseph: Ancient Persia. New York: 1996. I.B. Tauris. Recommends the use by scholars of the term Aryan to describe the Eastern, not the Western, branch of the Indo-European peoples (see "Aryan" in index)
- ^ Durant, Will: Our Oriental Heritage. New York: 1954. Simon and Schuster. According to Will Durant on Page 286: "the name Aryan first appears in the [name] Harri, one of the tribes of the Mitanni. In general it was the self-given appellation of the tribes living near or coming from the [southern] shores of the Caspian sea. The term is properly applied today chiefly to the Mitannians, Hittites, Medes, Persians, and Vedic Hindus, i.e., only to the eastern branch of the Indo-European peoples, whose western branch populated Europe."
- ^ Häkkinen, Jaakko (2012). "Early contacts between Uralic and Yukaghir". In Tiina Hyytiäinen; Lotta Jalava; Janne Saarikivi; Erika Sandman (eds.). Per Urales ad Orientem (Festschrift for Juha Janhunen on the occasion of his 60th birthday on 12 February 2012) (PDF). Helsinki: Finno-Ugric Society. ISBN 978-952-5667-34-9. Retrieved 12 November 2013.
- ^ Häkkinen, Jaakko (23 September 2012). "Problems in the method and interpretations of the computational phylogenetics based on linguistic data – An example of wishful thinking: Bouckaert et al. 2012" (PDF). Jaakko Häkkisen puolikuiva alkuperäsivusto. Jaakko Häkkinen. Retrieved 12 November 2013.
- ^ Cavalli-Sforza, Luigi Luca; Menozzi, Paolo; Piazza, Alberto (1994), The History and Geography of Human Genes, Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, p. See "Aryan" in index, ISBN 978-0-691-08750-4
- ^ Anthony 2007, p. 49.
- ^ أ ب Bryant 2001, p. 206.
- ^ أ ب ت ث Bryant 2001, p. 207.
- ^ Parpola 2015, p. 76.
- ^ Anthony & Vinogradov (1995); Kuzmina (1994), Klejn (1974), and Brentjes (1981), as cited in Bryant (2001:206)
- ^ أ ب Mallory 1989
- ^ Christopher I. Beckwith (2009), Empires of the Silk Road, Oxford University Press, p.30
- ^ Gening, V.F. The Cemetery at Sintashta and the Early Indo-Iranian People. Journal of Indo-European Studies 7, 1979, 1–29; cf. Gening, Mogil'nik Sintashta i problema rannikh Indoiranskikh plemen. Sovietskaya Arkheologiya 1977, 53–73
- ^ Burrow 1973.
- ^ أ ب Mallory & Mair 2000
- ^ Rigveda – Britannica Online Encyclopedia
- ^ Brzezinski, Richard; Mielczarek, Mariusz (2002). The Sarmatians, 600 BC-AD 450. Osprey Publishing. p. 39.
(..) Indeed, it is now accepted that the Sarmatians merged in with pre-Slavic populations.
- ^ Adams, Douglas Q. (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. Taylor & Francis. p. 523.
(..) In their Ukrainian and Polish homeland the Slavs were intermixed and at times overlain by Germanic speakers (the Goths) and by Iranian speakers (Scythians, Sarmatians, Alans) in a shifting array of tribal and national configurations.
- ^ Atkinson, Dorothy; et al. (1977). Women in Russia. Stanford University Press. p. 3.
(..) Ancient accounts link the Amazons with the Scythians and the Sarmatians, who successively dominated the south of Russia for a millennium extending back to the seventh century B.C. The descendants of these peoples were absorbed by the Slavs who came to be known as Russians.
- ^ Slovene Studies. Vol. 9–11. Society for Slovene Studies. 1987. p. 36.
(..) For example, the ancient Scythians, Sarmatians (amongst others), and many other attested but now extinct peoples were assimilated in the course of history by Proto-Slavs.
- ^ أ ب ت Gnoli, Gherardo (March 29, 2012). "Indo-Iranian Religion". Encyclopædia Iranica. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ Searle, Mike (28 March 2013). Colliding Continents: A geological exploration of the Himalaya, Karakoram, and Tibet. OUP Oxford. ISBN 978-0-19-165249-3.
- ^ Camerapix (1998). Spectrum Guide to Pakistan. Interlink Books. ISBN 978-1-56656-240-9.
- ^ Strand, Richard F. (31 December 2005). "Richard Strand's Nuristân Site: Peoples and Languages of Nuristan". nuristan.info. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 19 January 2012.
- ^ "The Kalash: Pakistan's last animist tribe". Atalayar (in الإنجليزية). 29 March 2021. Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- ^ Pelton, Robert Young (1 January 1997). Fielding's The World's Most Dangerous Places. Fielding Worldwide. ISBN 978-1-56952-140-3.
The Kalash (which means 'black' because of the black garments they wear) are an animist tribe who live in a region sometimes called Kafiristan.
- ^ Witzel, Michael (2012). The Origin of the World's Mythologies.
- ^ Witzel, Michael (2005). Vala and Iwato: The Myth of the Hidden Sun in India, Japan, and beyond (PDF).
- ^ Michael Witzel. "Kalash Religion" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 February 2022. Retrieved 14 March 2022 – via HUIT.
- ^ أ ب "THE DAEVAS IN ZOROASTRIAN SCRIPTURE" (PDF). University of Missouri System. Retrieved 2023-12-24.
- ^ "Saraswati Palaeochannels". bhuvan-app1.nrsc.gov.in. Retrieved 23 December 2023.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د Muesse, Mark W. (2011). The Hindu Traditions: A Concise Introduction (in الإنجليزية). Fortress Press. pp. 30–38. ISBN 978-1-4514-1400-4. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ ر ز س ش ص ض ط ظ ع غ ف ق ك ل م ن هـ و ي أأ أب أت أث أج أح أخ أد أذ Griswold, H. D.; Griswold, Hervey De Witt (1971). The Religion of the Ṛigveda. Motilal Banarsidass Publishe. pp. 1–21. ISBN 978-81-208-0745-7. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ The Sacred Books of the East: The Zend-Avesta, pt. I (in الإنجليزية). Clarendon Press. 1880. p. LVIII. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- ^ Mani, Chandra Mauli (2005). A Journey Through India's Past (in الإنجليزية). Northern Book Centre. p. 10. ISBN 978-81-7211-194-6. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح Muir, John (1874). Original Sanskrit Texts on the Origin and History of the People of India, Their Religion and Institutions (in الإنجليزية). Vol. 2. Trübner. p. 224. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ^ Bonar, Horatius (1884). The Life and Work of the Rev. G. Theophilus Dodds: Missionary in Connection with the McAll Mission, France (in الإنجليزية). R. Carter. p. 425. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ^ Kainiraka, Sanu (2016). From Indus to Independence: A Trek Through Indian History (in الإنجليزية). Vol. I: Prehistory to the Fall of the Mauryas. Vij Books India. ISBN 978-93-85563-14-0. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ^ Kala, Aporva (2015). Alchemist of the East (in الإنجليزية). Musk Deer. ISBN 978-93-84439-66-8. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ^ Braga, Teófilo (2013). Formação do Amadis de Gaula (in البرتغالية البرازيلية). Imprensa Portugueza. p. 36. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- ^ Lalueza-Fox, C.; Sampietro, M. L.; Gilbert, M. T.; Castri, L.; Facchini, F.; Pettener, D.; Bertranpetit, J. (2004). "Unravelling migrations in the steppe: Mitochondrial DNA sequences from ancient central Asians". Proceedings. Biological Sciences. 271 (1542): 941–947. doi:10.1098/rspb.2004.2698. PMC 1691686. PMID 15255049.
المصادر
- Anthony, David W. (2007), The Horse The Wheel And Language. How Bronze-Age Riders From the Eurasian Steppes Shaped The Modern World, Princeton University Press
- Bryant, Edwin (2001), The Quest for the Origins of Vedic Culture: The Indo-Aryan Migration Debate, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-513777-4
- Burrow, T. (1973), "The Proto-Indoaryans", Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland (2): 123–140
- Diakonoff, Igor M.; Kuz'mina, E. E.; Ivantchik, Askold I. (1995), "Two Recent Studies of Indo-Iranian Origins", Journal of the American Oriental Society (American Oriental Society) 115 (3): 473–477, doi:.
- Jones-Bley, K.; Zdanovich, D. G. (eds.), Complex Societies of Central Eurasia from the 3rd to the 1st Millennium BC, 2 vols, JIES Monograph Series Nos. 45, 46, Washington D.C. (2002), ISBN 0-941694-83-6, ISBN 0-941694-86-0.
- Kuz'mina, Elena Efimovna (1994), Откуда пришли индоарии? (Whence came the Indo-Aryans), Moscow: Российская академия наук (Russian Academy of Sciences).
- Kuz'mina, Elena Efimovna (2007), Mallory, James Patrick, ed., The Origin of the Indo-Iranians, Leiden Indo-European Etymological Dictionary Series, Leiden: Brill
- Mallory, J.P. (1989), In Search of the Indo-Europeans: Language, Archaeology, and Myth, London: Thames & Hudson.
- Mallory, J. P.; Adams, Douglas Q. (1997), "Indo-Iranian Languages", Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture, Fitzroy Dearborn.
- Mallory, J. P.; Mair, Victor H. (2000), The Tarim Mummies: Ancient China and the Mystery of the Earliest People from the West, London: Thames & Hudson.
- Parpola, Asko (1999), "The formation of the Aryan branch of Indo-European", in Blench, Roger; Spriggs, Matthew, Archaeology and Language, III: Artefacts, languages and texts, London and New York: Routledge.
- Sulimirski, Tadeusz (1970), Daniel, Glyn, ed., The Sarmatians, Ancient People and Places, Thames & Hudson, ISBN 0-500-02071-X
- Witzel, Michael (2000), "The Home of the Aryans", in Hintze, A.; Tichy, E., Anusantatyai. Fs. für Johanna Narten zum 70. Geburtstag, Dettelbach: J.H. Roell, pp. 283–338.
- Chopra, R. M., "Indo-Iranian Cultural Relations Through The Ages", Iran Society, Kolkata, 2005.
وصلات خارجية
- The Origin of the Pre-Imperial Iranian People by Oric Basirov (2001)
- The Origin of the Indo-Iranians Elena E. Kuz'mina. Edited by J.P. Mallory (2007)
- جميع الصفحات التي تحتاج تنظيف
- مقالات بالمعرفة تحتاج توضيح from July 2019
- CS1 البرتغالية البرازيلية-language sources (pt-br)
- مقالات ذات عبارات بحاجة لمصادر
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles with unsourced statements from July 2010
- Articles containing لاتينية-language text
- Articles with unsourced statements from January 2016
- الشعوب القديمة في آسيا
- جماعات بدوية في أوراسيا
- الشعوب الهندو-إيرانية