القوات البحرية البرازيلية
القوات البحرية البرازيلية (برتغالية: Marinha do Brasil، ويعني حرفيًا "بحرية البرازيل") هي البحرية التابعة للقوات المسلحة البرازيلية، والمسئولة عن العمليات البحرية. تعتبر البحرية البرازيلية أكبر بحية في أمريكا الجنوبية وأمريكا اللاتينية، وثاني أكبر بحرية في الأمريكاتين، بعد القوات البحرية الأمريكية.[2]
أشتركت البحرية في حرب استقلال البرازيل، نقلت معظم قوات البحرية البرتغالية والقواعد في أمريكا الجنوبية إلى البلد المستقلة حديثًا حينها. في أوائل العقد عقب الاستقلال، احتفظت البلاد بقوة بحرية كبيرة وشاركت البحرية لاحقًا في حرب السيزبلاتين، وصراعات ريو دى لابلاتا، وحرب پاراگواي بالإضافة إلى ثورات متفرقة أخرى تركت أثرًا بارزًا في تاريخ البرازيل.
بحلول ثمانينات القرن الاسع عشر أصبحت البحرية الأمبراطروية البرازيلية الأقوى في أمريكا الجنوبية. بعد قورة البحري 1893-1894، كانت هناك فجوة في تطوير البحرية حتى عام 1905، عندما استحوذت البرازيل على اثنان من أقوى وأحدث بارجة المدرعات في ذلك الوقت مما أشعل منافسة مدرعات مع جيران البرازيل في أمريكا الجنوبية. شاركت البحرية البرازيلية في كل من الحرب العالمية الأولى والحرب العالمية الثانية، وانخرطت في في دوريات ضد الغواصات في المحيط الأطلسي.
تشتمل البحرية البرازيلية الحديثة على صاروخ موجه بريطاني الصنع فرقاطات (FFG)، و حراقات (FFL)، وغواصات تعمل بالكهرباء والديزل الساحلي (SSK)و زوارق دوريات الساحلية والأنهار.
المهمة
بالإضافة إلى أدوار البحرية التقليدية، تقوم البحرية البرازيلية أيضًا بتنظيم البحرية التجارية ومهام السلامة التشغيلية الأخرى التي يقوم بها عادة خفر السواحل، مثل:
- تطبيق السياسة البحرية الوطنية
- تنفيذ وتطبيق القوانين والأنظمة المتعلقة بالبحر والمياه الداخلية.].
التاريخ
Origins
War of Independence
Cisplatine War and rebellions (1825–1849)
Platine & Paraguayan wars (1849–1870)

Expansion and the end of the Empire (1870–1889)
Early republic (1889–1917)

Revolt of the Lash

World Wars (1917–1945)
First World War (1917–1918)
Second World War (1942–1945)


Cold War period (1945–2000)
Lobster War (1961–1963)

1964 Coup d'état
Peacekeeping and SAR missions (2000–present)
Notable search and rescue missions
AFF447 (2009)

ARA San Juan (2017)
Peacekeeping operations (2004–present)
Haiti
Lebanon

Personnel
Ships and submarines


Aircraft
Marines
Current Brazilian fleet
Riachuelo, Scorpène-class submarine with changes in size and tonnage in 2020.
Rademaker, Type 22 frigate, in operation tropicalex 2016.
A Brazilian Bocaina, River-class minesweeper.
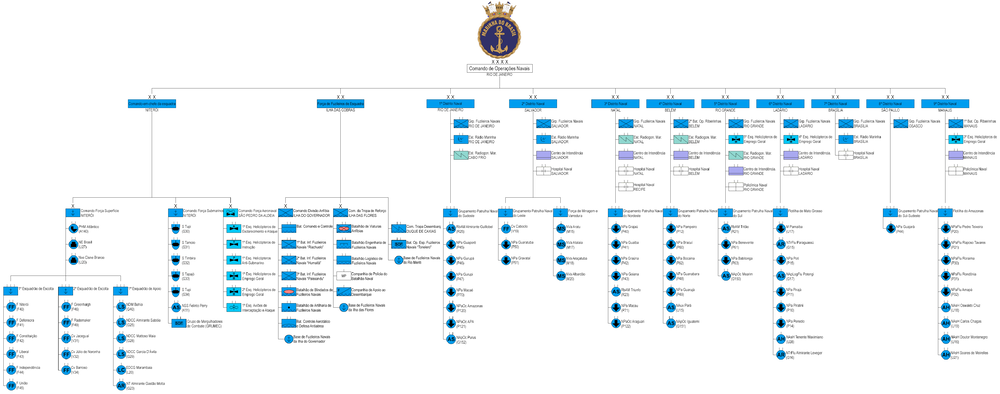
Structure and organisation
Branches

Structure

National Squadron

See also
- Armed Forces of the Empire of Brazil
- Imperial Brazilian Navy
- Naval Revolt
- Brazilian Marine Corps
- Brazilian Naval Aviation
- Brazilian Army
- Brazilian Air Force
- Military history of Brazil
- Military ranks of Brazil
- Brazil and weapons of mass destruction
- List of Brazilian Ministers of the Navy
مرئيات
| سفن حربية برازيلية تحاصر لبنان بحجة تدريب القوات الدولية، 21 أغسطس 2021. |
Notes
References
- ^ (in pt)Comandante da Marinha confirma nova esquadra no Nordeste, Marinha do Brasil, 2009-01-26, https://www.mar.mil.br/menu_v/sinopse/Complemento/complemento_26012009.htm, retrieved on 2009-02-01.
- ^ "Oceanographic and Meteorological Data Buoys", Hydro International, http://www.hydro-international.com/news/id2504-Oceanographic_and_Meteorological_Data_Buoys.html, retrieved on 2009-06-10.
Sources
- Carey, Alan C. (2004). Galloping Ghosts of the Brazilian Coast. Lincoln, NE USA: iUniverse, Inc. ISBN 978-0-595-31527-7.قالب:Self-published source
- Doratioto, Francisco (2002). Maldita Guerra: Nova história da Guerra do Paraguai [Cursed War: New War history of Paraguay] (in البرتغالية). São Paulo: Companhia das Letras.
- Ehlers, Hartmut (2004). "The Paraguayan Navy: Past and Present, Part II". Warship International. XLI (2): 173–206. ISSN 0043-0374.
- English, Adrian J. (1984). Jane's Armed Forces of Latin America. London and New York: Jane's. ISBN 978-0-7106-0321-0. OCLC 11537114.
- Garrett, James L (Autumn 1985). "The Beagle Channel Dispute: Confrontation and Negotiation in the Southern Cone". Journal of Interamerican Studies and World Affairs. 27 (3): 81–109. doi:10.2307/165601. JSTOR 165601..
- Grant, Jonathan A (Mar 2007). Rulers, Guns & Money: The Global Arms Trade in the Age of Imperialism (hardback). Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-02442-7..
- de Holanda, Sérgio Buarque (1974). Declínio e queda do Império [Decline and Fall of the Empire]. História Geral da Civilização Brasileira (in البرتغالية) (2 ed.). São Paulo: Difusão européia do livro.
- Janotti, Maria de Lourdes Monaco (1986). Os Subversivos da República [The Republic’s subversives] (in البرتغالية). São Paulo: Brasiliense.
- Livermore, Seward W (Mar 1944). "Battleship Diplomacy in South America: 1905–1925". The Journal of Modern History. 16 (1): 31–48. doi:10.1086/236787. JSTOR 1870986. S2CID 145007468..
- Love, Joseph L (2012). The Revolt of the Whip. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-8109-1. OCLC 757838402..
- Maia, Prado (1975). A Marinha do Brasil na colônia e no Império [The Navy of Brazil in the Colony and the Empire] (in البرتغالية) (2 ed.). Rio de Janeiro: Cátedra.
- Martins, João Roberto filho (2007). "Colossos do mares" [Sea colossuses]. Revista de História da Biblioteca Nacional. 3 (27): 74–77. ISSN 1808-4001. OCLC 61697383..
- Martins, João Roberto filho (2010). A marinha brasileira na era dos encouraçados, 1885–1910: tecnologia, Forças Armadas e política [The Brazilian Navy in the ironclads era, 1885–1910: technology, armed forces & politics] (in البرتغالية). Rio de Janeiro: FGV. ISBN 978-85-225-0803-7. OCLC 679733899..
- Morgan, Zachary R (2003). "The Revolt of the Lash, 1910". In Bell, Christopher M; Elleman, Bruce A (eds.). Naval Mutinies of the Twentieth Century: An International Perspective. Portland, OR: Frank Cass. pp. 32–53. ISBN 978-0-7146-8468-0. OCLC 464313205..
- Morison, Samuel Eliot (1947). History of United States Naval Operations in World War II: The Battle of the Atlantic; September 1939 – May 1943. Boston: Little Brown. ISBN 978-0-252-06963-5.
- Scheina, Robert L (1984). "Brazil". In Gardiner, Robert; Gray, Randal (eds.). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships: 1906–1921. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. pp. 403–7. ISBN 978-0-87021-907-8. OCLC 12119866..
- Scheina, Robert L (1987). Latin America: A Naval History, 1810–1987 (ill ed.). Annapolis, MD: Naval Inst Press. ISBN 978-0-87021-295-6. OCLC 15696006..
- Schwarcz, Lilia Moritz (2002) (in pt), As Barbas do Imperador: D. Pedro II, um monarca nos trópicos (2 ed.), São Paulo: Companhia das Letras.
- de St. Hubert, Christian (1991). "Question 34/88". Warship International. XXVIII (2): 198–199. ISSN 0043-0374.
- Topliss, David (1988). "The Brazilian Dreadnoughts, 1904–1914". Warship International. 25 (3): 240–89. ISSN 0043-0374. OCLC 1647131..
وصلات خارجية
- Brazilian Navy Official website (in برتغالية)
- Poder Naval Brazilian warships and naval aviation (in برتغالية)
- Official histories of Brazilian ships (in برتغالية)
- Global Security Brazilian Navy profile
- History of World's Navy's Ships of the Brazilian Navy
- History of VF-1 "Falcões" (Hawks) in the Brazilian Navy
- Brazilian naval flags
- Base Militar Web Magazine's Brazilian military aircraft data base
- Military Orders and Medals from Brazil (in برتغالية)
Videos
- Articles containing إنگليزية-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Articles containing برتغالية-language text
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Pages with empty portal template
- CS1 البرتغالية-language sources (pt)
- Articles with برتغالية-language sources (pt)
- القوات البحرية البرازيلية