البريمية
Leptospira
| Leptospira | |
|---|---|
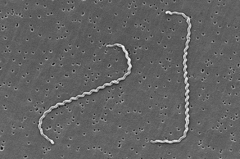
| |
| Scanning electron micrograph of Leptospira interrogans. | |
| التصنيف العلمي | |
| Domain: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Leptospira Noguchi 1917
|
| Species | |
|
L. alexanderi L. genomospecies 1 | |
Leptospira (Greek leptos, "fine, thin" and Latin spira, "coil")[1] is a genus of spirochaete bacteria, including a small number of pathogenic and saprophytic species.[2] Leptospira was first observed in 1907 in kidney tissue slices of a leptospirosis victim who was described as having died of "yellow fever."[3]
صفاتها
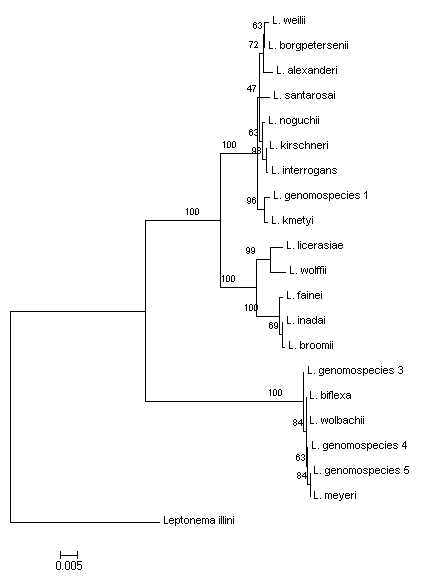
تم استنتاج التاريخ التطوري باستخدام طريقة أقل تطور [4]. The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 1000 replicates is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed [5]. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 50% bootstrap replicates are collapsed. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site [6]. The ME tree was searched using the Close-Neighbor-Interchange (CNI) algorithm at a search level of 1 [7]. اُستُخدمت خوارزمية الارتباط بالجار لتوليد الشجرة المبدئية. Codon positions included were 1st+2nd+3rd+Noncoding[8]. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated from the dataset (Complete deletion option). There were a total of 1254 positions in the final dataset. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted in MEGA4 [9].
- شكلها لولبي، طولها 2 ميكرون، عرضها 0.1 ميكرون.
- متحركة و لها سوطين نهائيين.
- لا ترى بالمجهر العادي بل مجهر القعر المظلم.
- هوائية مخيرة.
- تنمو على الأوساط الغنية الحاوية على مصل وبروتينات، وتحتاج ضغط %10 CO2.
- النوع الممرض فيها هو: Leptospira Icterohemorahgrae يسبب مرض اليرقان النزفي.
- يدخل الجرثوم للجسم عبر سحجات الجلد أو الأغشية المخاطية، وخاصة المياه الملوثة بالمسابح أو الحقل أو الأنهر، ويمكن أن يدخل من الطين من بين أصابع القدمين، ومن الأتربة الملوثة.
- مقاوم للبيئة، يمكن أن يعيش فترات طويلة بالبيئة حتى لو جفت وعندما تعود المياه يعود ليعيش.
- بعد دخول الجرثوم، يمكن أن يمر بفترة حضانة طويلة نسبياً تختلف حسب الشخص وحسب الجرثوم ولذلك تختلف شدة الإصابة.
- يمكن أن يسبب أعراض يرقان أو التهاب بول لأن الجرثوم يطرح عن طريق البول ويمكن أن يؤدي لانحلال دم خفيف لأن الجرثوم له قدرة على حل كريات الدم الحمراء.
المرضية البريمية
- Leptospira interrogans
- Leptospira kirschneri
- Leptospira noguchii
- Leptospira alexanderi
- Leptospira weilii
- Leptospira genomospecies 1
- Leptospira borgpetersenii
- Leptospira santarosai
- Leptospira kmetyi[10]
الأعراض:
حرقة بول ـ تخريش المخاطيات البولية ـ التهاب مجرى البول ـ التهاب دم ـ انحلال دم يؤدي إلى فقر دم وظهور كريات دم بيضاء وحمراء منحلة في البول.
- عندما تخرج هذه الجراثيم مع البول يمكن أن تذهب للمياه الملوثة، وتعتبر الفئران والجرذان مستودع لها، ولا سبب لها أعراض، وبالتالي تنتقل من منطقة لأخرى وتلوث المياه والمناطق الأخرى، فهي مستودع وطريق اتصال.
Genotyping
Genome sequence determination (of Leptospira) lead to the development of Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) based scheme for species level identification of pathogenic Leptospira species. The pioneering MLST method developed by Niyaz Ahmed in Hyderabad, India and colleagues[11] is widely used for molecular epidemiology studies and holds the potential to replace the highly ambiguous, serotyping method currently in vogue for leptospiral strain identification.
انظر أيضاً
الهامش
- ^ "leptospirosis". American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language: Fourth Edition. Bartleby.com. 2000. Retrieved 2007-05-13.
- ^ Ryan KJ; Ray CG (editors) (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. ISBN 0-8385-8529-9.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stimson AM (1907). "Note on an organism found in yellow-fever tissue." Public Health Reports 22:541.
- ^ Rzhetsky A & Nei M (1992) A simple method for estimating and testing minimum evolution trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution 9:945-967
- ^ Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783-791
- ^ Tamura, K., Nei, M. & Kumar S. (2004) Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. PNAS 101:11030-11035.
- ^ Nei M & Kumar S (2000) Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, New York
- ^ Saitou N & Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution 4:406-425
- ^ Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M & Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution 10.1093/molbev/msm092
- ^ Slack, A. T., Khairani-Bejo, S., Symonds, M. L., Dohnt, M. F., Galloway, R. L., Steigerwalt, A. G., Bahaman, A. R., Craig, S., Harrower, B. J. & other authors (2008). Leptospira kmetyi sp. nov., isolated from an environmental source in Malaysia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol In Press.
- ^ Ann-clinmicrob.com
وصلات خارجية
- Leptospira page at Kenyon College MicrobeWiki.
- Pasteur Institute - Leptospira Molecular Genetics Server
