الحمار الوحشي السهلي
(تم التحويل من حمار السهول الوحشي)
| الحمار الوحشي السهلي | |
|---|---|

| |
| الحمار الوحشي السهلي في محمية نگورونگورو، تنزانيا. | |
| التصنيف العلمي | |
| مملكة: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Subgenus: | |
| Species: | E. quagga
|
| Binomial name | |
| Equus quagga بودايرت، 1785
| |
| تحت الأنواع | |
|
E. q. quagga † | |
| |
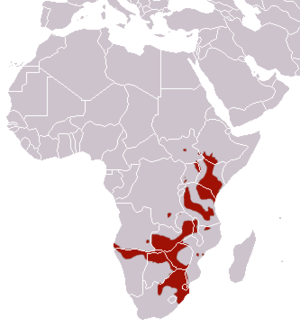
| نطاق انتشار الحمار الوحشي السهلي | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
الحمار الوحشي السهلي plains zebra (Equus quagga، سابقاً Equus burchellii)، ويعرف أيضاً الحمار الوحشي الشائع أو حمار برتشل الوحشي، هو أكثر أنواع الحمير الوحشية شيوعاً وانتشاراً جغرافياً.[2] ينتشر من جنوب إثيوپيا عبر شرق أفريقيا حتى أقصى جنوب بتسوانا وشرق جنوب أفريقيا. لا يزال الحمار الوحشي السهلي شائعاً في محميات الألعاب، لكنه مهدد بالأنشطة البشرية مثل اصطياده من أجل لحمه وجلده، والمنافسة مع الماشية وانتهاكه بالزراعة على معظم موائله.
التصنيف
تحت الأنواع
الوصف
وظيفة الخطوط
البيئة
الانتشار والموئل
النظام الغذائي
التفاعل مع الرعاة الآخرين
السلوك
البنية الاجتماعية
التواصل
التكاثر
السلوك
التفاعل مع البشر
الحفاظ
في الثقافة
المصادر
- ^ أ ب خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةiucn - ^ Grubb, P. (2005). "Order Perissodactyla". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 630. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
المراجع
- Alden, P. C., Estes, R. D., Schlitter, D., McBride, B. (1995). National Audubon Society Field Guide to African Wildlife. New York, Chanticleer Press, Inc. pg. 151
- Apps, P., du Toit, R. (2006). Creatures of Habit: Understanding African Animal Behaviour. Struik. pp. 74–75.
- Estes, R. (1991). The Behavior Guide to African Mammals, Including Hoofed Mammals, Carnivores, Primates. Los Angeles, University of California Press. pp. 242–246
- Groves, C. P.; Bell, H. B. (2004). "New investigations on the taxonomy of the zebras genus Equus, subgenus Hippotigris". Mammalian Biology. 69: 182–196. doi:10.1078/1616-5047-00133.
- Grubb, P. (1981). "Equus burchellii". Mammalian Species. 157: 1–9. doi:10.2307/3503962.
- قالب:IUCN2011.1 (extinct subspecies of the plains zebra.)
- Higuchi; et al. (1987). "Mitochondrial DNA of the Extinct Quagga: Relatedness and Extent of Postmortem Change". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 25: 283–287. doi:10.1007/BF02603111. PMID 2822938.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|first1=(help) - Kingdon, J. (1988). East African Mammals: An Atlas of Evolution in Africa, Volume 3, Part B: Large Mammals. Chicago, University of Chicago Press. pp. 165–179
- Klingel, H. (1969). "Reproduction in the plains zebra Equus burchelli boehmi: behaviour and ecological factors". J. Reprod. Fertil., Suppl. 6: 339–345.
- Moelman, P. D. (2002). Equids. Zebras, Assess and Horses. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. IUCN/SSC Equid Specialist Group. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland. Chapter 4. Status and Action Plan for the Plains Zebra (Equus burchelli). Mace A. Hack, Rod East and Dan J Rubenstein. pp. 43–57.
- Moehlman, P. D. (2003). Grizmek's Animal Life Encyclopedia. Mammals IV. Detroit, The Gale Group, Inc. 15.
- Moss, C., Ed. (1982). Portraits in the Wild, Animal Behavior in East Africa. Chicago, University of Chicago Press.
- Prothero, D. R.; Schoch, R. M. (2003). Horns, Tusks, and Flippers: The Evolution of Hoofed Mammals. Johns Hopkins University Press.
- Rubenstein, D. I. & M. Hack (2004) Natural and sexual selection and the evolution of multi-level societies: insights from zebras with comparisons to primates. pp. 266–279. In: Sexual Selection in Primates: New and Comparative Perspectives. P. Kappeler and C. P. van Schaik (eds.). Cambridge University Press.
وصلات خارجية
توجد في معرفةالفصائل معلومات أكثر حول:
 وسائط متعلقة بـEquus quagga من مشاع المعرفة.
وسائط متعلقة بـEquus quagga من مشاع المعرفة.
الكلمات الدالة:
This article contains content from Wikimedia licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Please comply with the license terms.












