ستورتنگ
ستورتنگ (Storting ؛ نرويجية: Stortinget [ˈstûːʈɪŋə]؛ "المجلس الأكبر") هو المجلس التشريعي الأعلى للنرويج، تأسس في 1814 تنفيذاً لدستور النرويج. ويوجد في أوسلو. The unicameral parliament has 169 members, and is elected every four years based on party-list proportional representation in nineteen multi-seat constituencies. A member of Stortinget is known in Norwegian as a stortingsrepresentant, literally "Storting representative".[2]
برلمان النرويج ستورتنگت | |
|---|---|
| الستورتنگ رقم 165 | |
 | |
| النوع | |
| النوع | |
| أقصى مدد | 4 سنوات |
| تأسس | 1814 |
| الزعامة | |
| الهيكل | |
| المقاعد | 169 (85 needed for majority) |
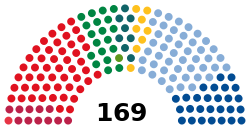 | |
المجموعات السياسية | الحكومة (61)
Opposition (108)
|
| اللجان |
|
| الانتخابات | |
| Open list proportional representation Modified Sainte-Laguë method | |
آخر انتخابات | 11 سبتمبر 2017 |
الانتخابات المقبلة | 13 سبتمبر 2021 |
| مكان الانعقاد | |
 | |
| مبنى برلمان النرويج أوسلو، النرويج | |
| الموقع الإلكتروني | |
| stortinget | |
| الدستور | |
| دستور النرويج | |
The assembly is led by a president and, since 2009, five vice presidents: the presidium. The members are allocated to twelve standing committees, as well as four procedural committees. Three ombudsmen are directly subordinate to parliament: the Parliamentary Intelligence Oversight Committee and the Office of the Auditor General.
Parliamentarianism was established in 1884, with the Storting operating a form of "qualified unicameralism", in which it divided its membership into two internal chambers making Norway a de facto bicameral parliament, the Lagting and the Odelsting.[3] Following a constitutional amendment in 2007, this was abolished, taking effect following the 2009 election.[4]
Following the 2017 election, nine parties are represented in parliament: the Labour Party (49 representatives), the Conservative Party (45), the Progress Party (27), the Centre Party (19), the Christian Democratic Party (8), the Liberal Party (8), the Socialist Left Party (11), the Green Party (1) and the Red Party (1). Since 2018, Tone Wilhelmsen Trøen has been President of the Storting.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التنظيم
الرئاسة
The presidium is chaired by the President of the Storting, consisting of the president and five vice presidents of the Storting. The system with five vice presidents was implemented in 2009. Before this there was a single holder of the office.[5][6]
| المنصب | الممثل | الحزب |
|---|---|---|
| الرئيس | Tone W. Trøen | المحافظين |
| النائب الأول للرئيس | Eva Kristin Hansen | العمال |
| النائب الثاني للرئيس | مورتن ڤولد | Progress |
| النائب الثالث للرئيس | Magne Rommetveit | العمال |
| النائب الرابع للرئيس | Nils T. Bjørke | Centre |
| النائب الخامس للرئيس | Ingjerd Schou | Conservative |
اللجان المنعقدة
The members of parliament are allocated into twelve standing committees, of which eleven are related to specific political topics. The last is the Standing Committee on Scrutiny and Constitutional Affairs. The standing committees have a portfolio that covers that of one or more government ministers.[7]
| اللجنة | الرئيس | حزب الرئيس |
|---|---|---|
| Business and Industry | Geir Pollestad | Centre |
| Education, Research and Church Affairs | Roy Steffensen | Progress |
| Energy and the Environment | Ketil Kjenseth | Liberal |
| Family and Cultural Affairs | Kristin Ørmen Johnsen | Conservative |
| Finance and Economic Affairs | مدثر كاپور | محافظين |
| Foreign Affairs and Defence | Anniken Huitfeldt | Labour |
| Health and Care Services | Geir Jørgen Bekkevold | Christian Democratic |
| Justice | Lene Vågslid | Labour |
| Labour and Social Affairs | Erlend Wiborg | Progress |
| Local Government and Public Administration | Karin Andersen | Socialist Left |
| Scrutiny and Constitutional Affairs | Dag Terje Andersen | Labour |
| Transport and Communications | Helge Orten | Conservative |
لجان أخرى
There are four other committees, that run parallel to the standing committees. The Enlarged Committee on Foreign Affairs consists of members of the Standing Committee on Foreign Affairs and Defence, the presidium, and the parliamentary leaders. The committee discusses important issues related to foreign affairs, trade policy, and national safety with the government. Discussions are confidential. The European Committee consists of the members of the Standing Committee on Foreign Affairs and Defence and the parliamentary delegation to the European Economic Area (EEA) and the European Free Trade Area (EFTA). The committee conducts discussions with the government regarding directives from the European Union.
The Election Committee consists of 37 members, and is responsible for internal elections within the parliament, as well as delegating and negotiating party and representative allocation within the presidium, standing committees, and other committees. The Preparatory Credentials Committee has 16 members and is responsible for approving the election.
جماعات الأحزاب
Each party represented in parliament has a party group. It is led by a group board and chaired by a parliamentary leader. It is customary for the party leader to also act as parliamentary leader, but since party leaders of government parties normally sit as ministers, governing parties elect other representatives as their parliamentary leaders. The table reflects the results of the September 2017 election.
| الحزب | المقاعد | الزعيم البرلماني |
|---|---|---|
| حزب العمال | 49 | يوناس گار ستورى (also party leader)[8] |
| Progress Party | 27 | Siv Jensen (also party leader)[9] |
| Conservative Party | 45 | Trond Helleland[10] |
| Socialist Left Party | 11 | Audun Lysbakken (also party leader)[11] |
| Centre Party | 19 | Marit Arnstad[12] |
| Christian Democratic Party | 8 | Hans Fredrik Grøvan[13] |
| Liberal Party | 8 | Terje Breivik[14] |
| Green Party | 1 | Une Bastholm (also party leader)[15] |
| Red Party | 1 | Bjørnar Moxnes (also party leader)[16] |
الانتخابات
انظر أيضاً
الهامش
- ^ Stensland, Marianne. "Mangler du oversikt? Slik var den historiske dagen Frp varslet regjeringsexit". Aftenposten. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ^ Stortingsrepresentant ulovlig pågrepet, NTB, Dagens Næringsliv, 18 August 2016
- ^ Scandinavian Politics Today, David Arter, Manchester University Press, 1999, page 31
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةECHR - ^ Stortinget.no
- ^ "Stortingets presidentskap". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2020-01-31. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ "Representanter og komiteer". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2008-03-27. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ "Arbeiderpartiet (A)". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2019-10-02. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ "Fremskrittspartiet (FrP)". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2019-10-02. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ "Høyre (H)". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2019-10-02. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ "Sosialistisk Venstreparti (SV)". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2019-10-02. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ "Senterpartiet (Sp)". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2019-10-02. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ "Kristelig Folkeparti (KrF)". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2019-10-02. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ "Venstre (V)". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2020-02-03. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ "Miljøpartiet De Grønne (MDG)". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2020-02-07. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
- ^ "Rødt (R)". Stortinget (in النرويجية). 2019-10-02. Retrieved 2020-05-17.
وصلات خارجية
- Media related to ستورتنگ at Wikimedia Commons
- Official website (in English)
- Ekspert om opplysningsplikten: Slik er reglene for hva statsråder må fortelle i Stortinget [expert about opplysningsplikten (or obligation to disclose): Such are the rules for ministers, in regard to what (they) must tell Stortinget] (20 November 2020) Dagsavisen
قالب:Storting قالب:Norwegian elections
Coordinates: 59°54′46.20″N 10°44′24.52″E / 59.9128333°N 10.7401444°E