نبق
| نبق Buckthorn | |
|---|---|

| |
| Alder Buckthorn (Rhamnus frangula) | |
| التصنيف العلمي | |
| مملكة: | |
| Division: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | نبقيات |
| Species | |
|
See text. | |
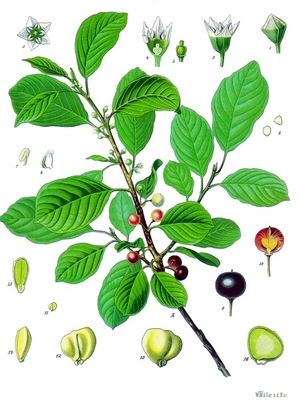
النبق (بالإنجليزية : Buckthorn) وهي ثمار شجرة السدر وهي شجيرة ساقطة الأوراق, تحمل فروعها أشواكا في نهايتها, وأوراقها مدورة بيضوية حادة النهاية مسننة الحافة ولها قشيرة سميكة, ولها معلاق كما تكون متقابلة على الساق. تتكون الأزهار في ابط الأوراق بعدد يتراوح بين 10 و15 زهرة, والأزهار صغيرة بيضاء مخضرة اللون, والثمار كرزية غضة مرة الطعم, سوداء عند النضج وفيها 3 - 4 بذور. يعيش النبق في المناطق الجبلية وعلى ضفاف الأنهار وينتشر بشكل واسع في منطقة حوض البحر الأبيض المتوسط. وقيل أن اكليل المسيح ضفر من شوك هذا النبات. [1]
مكونات الثمار
تحتوي ثمار النبق على غليكوزيدات انتراكينونية أهمها الرامنوكاثرين كما تحتوي على الفرانغولا ايمودين والرامنوكسانتين إلى جانب غليكوزيدات فلافونوئيدية أهمها الكويرسيتين, وفيتامين سي وتحتوي القشرة على الرامنكوزيد بنسبة 7.4 % وحمض الكريزوفاني.
الإستعمال الطبي
يستعمل مغلي الثمار كمادة مسهلة نظرا لوجود الغليكوزيدات الإنتراكينونية كما أنها مدرة للبول ومنقية للدم, وتدخل خلاصة الثمار في العديد من الأشكال الصيدلانية الملينة والمسهلة.
التصنيف
The genus is divided into two subgenera, sometimes treated as separate genera:
- Subgenus Rhamnus: flowers with four petals, buds with bud scales, leaves opposite or alternate, branches with spines. Species include:
- Rhamnus alaternus – Italian Buckthorn
- Rhamnus alnifolia – Alderleaf Buckthorn
- Rhamnus arguta – Sharp-tooth Buckthorn
- Rhamnus cathartica – Common (or Purging) Buckthorn (syn. R. catharticus)
- Rhamnus crocea – Redberry Buckthorn (ssp. crocea), Hollyleaf Buckthorn (ssp. pilosa)
- Rhamnus davurica – Dahurian Buckthorn
- Rhamnus diffusus
- Rhamnus globosa – Lokao Buckthorn
- Rhamnus ilicifolia – Hollyleaf Redberry
- Rhamnus japonica – Japanese Buckthorn
- Rhamnus lanceolata – Lanceleaf Buckthorn
- Rhamnus libanotica
- Rhamnus lycioides
- Rhamnus petiolaris - endemic to Sri Lanka
- Rhamnus pirifolia – Island Redberry Buckthorn
- Rhamnus prinoides – Shiny-leaf Buckthorn
- Rhamnus saxatilis – Rock Buckthorn, Avignon Buckthorn, Avignon Berry (syn. R. infectoria, R. infectorius)
- Rhamnus serrata – Sawleaf Buckthorn
- Rhamnus smithii – Smith's Buckthorn
- Rhamnus staddo – Staddo (syn. R. rhodesicus)
- Rhamnus tinctoria - Dyer's Buckthorn (syn. R. saxatilis ssp. tinctorius)
- Rhamnus utilis – Chinese Buckthorn
- Subgenus Frangula: flowers with five petals, buds without bud scales, leaves always alternate, branches without spines. Species include:
- Rhamnus betulaefolia (Frangula betulifolia) – Birchleaf Buckthorn
- Rhamnus californica (Frangula californica) – California Buckthorn, Coffeeberry
- Rhamnus caroliniana (Frangula caroliniana) – Carolina Buckthorn, Indian Cherry (syn. R. carolinianus)
- Rhamnus frangula (Frangula alnus) – Alder Buckthorn, Glossy or Breaking Buckthorn, Black Dogwood
- Rhamnus glandulosa - Sanguinho
- Rhamnus latifolia (Frangula azorica)
- Rhamnus purshiana (Frangula purshiana) – Cascara Buckthorn (syn. R. purshianus)
- Rhamnus rubra (Frangula rubra) – Red Buckthorn
- Rhamnus sphaerosperma (Frangula sphaerosperma) – West Indian Buckthorn
The Purging Buckthorn or Common Buckthorn (R. cathartica) is a widespread European native species, in the past used as a purgative, though its toxicity makes this a very risky herbal medicine and it is no longer used. Introduced into the الولايات المتحدة as a garden shrub, this has become an invasive species in many areas there. It has recently been discovered to be a primary host of the soybean aphid Aphis glycines, a problem pest for soybean farmers across the US. The aphids use the buckthorn as a host for the winter and then spread to nearby soybean fields in the spring.
Another European species, Alder Buckthorn (R. frangula, syn. Frangula alnus) was of major military importance in the 15th to 19th centuries, as its wood provided the best quality charcoal for gunpowder manufacture.
Italian Buckthorn (R. alaternus), an evergreen species from the Mediterranean region, has become a serious weed in some parts of New Zealand—especially on Hauraki Gulf islands.
Dyer's Buckthorn (R. tinctoria) is used, together with the Asian Chinese Buckthorn (R. utilis), to produce the dye "china green". Another species, Avignon Buckthorn (R. saxatilis) provides the yellow dye Persian berry, made from the berries.
Sanguinho (R. glandulosa) is endemic to the Macaronesian islands, where it is found in the laurisilva forests of the Madeira and Canary Islands.
North American species include Alder-leaf Buckthorn (R. alnifolia) right across the continent, Carolina Buckthorn (R. (F.) caroliniana) in the east, Cascara Buckthorn (R. (F.) purshiana) in the west, and the evergreen California Buckthorn or Coffeeberry (R. (F.) californica) and Hollyleaf Buckthorn (R. crocea) in the west.
In South America, Rhamnus diffusus is a small shrub native from the Valdivian temperate rain forests in Chile.
Buckthorns may be confused with Dogwoods, which share the curved leaf venation; indeed, "dogwood" is a local name for R. prinoides in southern Africa, a plant used to make Ethiopian mead and known as "gesho" in Ethiopia. The two plants are easy to distinguish by slowly pulling a leaf apart; in dogwood thin white latex strings can be seen, strings not present in buckthorn.
وصلات خارجية
| Buckthorn
]].