ثدن
الثدن أو خلل التنسج Dysplasia، هو مصطلح يستخدم في علم الأنسجة للإشارة إلى التطور الغير طبيعي.[1] يستخدم المصطلح لوصف اضطراب الخلايا وعدم انتظامها، ولا يعد تكاثراً ورمياً، وإنما قد يكون مرحلة تسبق حدوث الورم (أو السرطان). وتحدث هذه الحالة في نسيج بشروي ما في الجسم.
الأسباب
أسباب الثدن كثيرة تتعلق بالمنطقة المصابة، يُذْكر منها: التدخين، والفيروسات التي تنتقل عن طريق الجنس، وبعض أنواع الالتهابات، وأسباب وراثية وغيرها. أما تقرير المعالجة فتتعلق بمنطقة الإصابة ومعرفة السبب، وتبقى الوقاية بالابتعاد عن الأسباب المحدثة.
تعريف
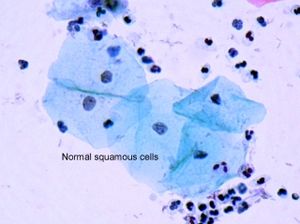
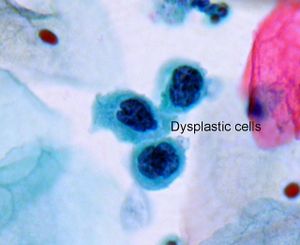
تكون الخلايا البشروية في حال الإصابة بالثدن ذات أشكال وأحجام مختلفة (عدم انتظام في شكلها وحجمها) وتكون نوى هذه الخلايا كبيرة الحجم مقارنة مع حجم الخلية، مع وجود انقسامات غير طبيعية فيها أحياناً كثيرة. وتبدو النوى كذلك شديدة التلون «عند مشاهدتها بالمجهر الضوئي، بعد تلوينها بالملونات الخاصة لدراستها». ومن جهة ثانية، يكون توضع هذه الخلايا بشكل غير منتظم (أو عشوائي).
تتوضع الخلايا في البشرة الطبيعية بانتظام من الطبقة القاعدية باتجاه الأعلى حيث تتمايز هذه الخلايا وتنضج، ولأسباب مختلفة قد يحدث عدم تمايز في هذه الخلايا وتضطرب في توضعها وتمايزها ونضجها. وعندما يشمل هذا الاضطراب وعدم الانتظام (مع وجود التبدلات الخلوية التي أُشير إليها) جميع طبقات البشرة يدعى الثدن في هذه الحالة بالسرطان اللابد carcinoma in situ وهي مرحلة قبيل سرطانية.
الدرجات
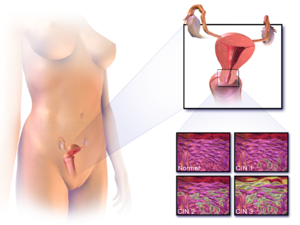
يقسم الثدن ثلاث درجات: درجة خفيفة ودرجة متوسطة ودرجة شديدة. والدرجات الخفيفة أو المتوسطة غالباً ما تتراجع إلى الحالة الطبيعية بعد المعالجة (أو غياب السبب)، أما الحالات الشديدة وهي السرطان اللابد فغالباً ما تتطور إلى سرطان غازي. [2]
أمثلة
كمثال على الثدن ثدن البشرة الثؤلولي في الجلد، ومرض بوفن، وثدن البشرة من عنق الرحم، وثدن البشرة في الرئة أو الجهاز التنفسي والحنجرة، وثدن البشرة في الجهاز الهضمي (من الفم وحتى الشرج)، وغيرها.
التغيرات المجهرية
الثدن الظهاري
| التنسج و-التغذية |
|---|
|
|
Epithelial dysplasia consists of an expansion of immature cells (such as cells of the ectoderm), with a corresponding decrease in the number and location of mature cells. Dysplasia is often indicative of an early neoplastic process. The term dysplasia is typically used when the cellular abnormality is restricted to the originating tissue, as in the case of an early, in-situ neoplasm.[citation needed]
Dysplasia, in which cell maturation and differentiation are delayed, can be contrasted with metaplasia, in which cells of one mature, differentiated type are replaced by cells of another mature, differentiated type.[citation needed]
متلازمة الثدن النقوي
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature and therefore do not become healthy blood cells.[3] Problems with blood cell formation result in some combination of low red blood cells, low platelets, and low white blood cells.[3] Some types have an increase in immature blood cells, called blasts, in the bone marrow or blood.[3]
ثدن العظام المتليف
Fibrous dysplasia of bone is a disorder where normal bone and marrow is replaced with fibrous tissue, resulting in formation of bone that is weak and prone to expansion. As a result, most complications result from fracture, deformity, functional impairment and pain.[4]
بالعين المجردة
خلل التنسج الوركي
Hip dysplasia is an abnormality of the hip joint where the socket portion does not fully cover the ball portion, resulting in an increased risk for joint dislocation.[5] Hip dysplasia may occur at birth or develop in early life.[5] Regardless, it does not typically produce symptoms in babies less than a year old.[6] Occasionally one leg may be shorter than the other.[5] The left hip is more often affected than the right.[6] Complications without treatment can include arthritis, limping, and low back pain.[6]
ثدن الكلى متعدد الكيسات
Multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK) is a condition that results from the malformation of the kidney during fetal development. The kidney consists of irregular cysts of varying sizes. Multicystic dysplastic kidney is a common type of renal cystic disease, and it is a cause of an abdominal mass in infants.[7]
الثدن والسرطان اللابد والسرطان الغازي
انظر أيضاً
الهوامش
- ^ "dysplasia" في قاموس دورلاند الطبي
- ^ وليد الصالح. "الثدن". الموسوعة العربية. Retrieved 2014-03-17.
- ^ أ ب ت "Myelodysplastic Syndromes Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient Version". NCI. 12 August 2015. Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- ^ Boyce AM, Florenzano P, de Castro LF, Collins MT (February 2015). "Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune–Albright Syndrome". In Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJ, Mirzaa G, Amemiya A (eds.). Gene Reviews. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle. PMID 25719192.
- ^ أ ب ت "Developmental Dislocation (Dysplasia) of the Hip (DDH)". American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. October 2013.
- ^ أ ب ت Shaw BA, Segal LS (December 2016). "Evaluation and Referral for Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip in Infants". Pediatrics. 138 (6): e20163107. doi:10.1542/peds.2016-3107. PMID 27940740.
- ^ Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney Imaging at eMedicine
المصادر
- Noel Weidner (editor), Richard Cote, Saul Suster, Lawrence Weiss (2003). Modern Surgical Pathology. London: W.B. Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-7253-1. OCLC 50244347.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Ramzi S. Cotran, Vinay Kumar, Tucker Collins (Editor) (1999). Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease (6th ed.). London: W.B. Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-7335-X. OCLC 39465455.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)