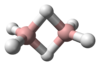بروميد الهيدروجين
| |||
|
| |||
| الأسماء | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك المفضل
Hydrogen bromide[بحاجة لمصدر] | |||
| اسم أيوپاك النظامي
Bromane[1] | |||
| المُعرِّفات | |||
| رقم CAS | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| مرجع بايلستاين | 3587158 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.090 | ||
| رقم EC |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
| عناوين مواضيع طبية MeSH | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| رقم RTECS |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1048 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| الخصائص | |||
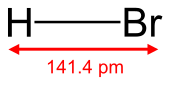
| الصيغة الجزيئية | HBr | ||
| كتلة مولية | 80.91 g/mol | ||
| المظهر | Colorless gas | ||
| الرائحة | Acrid | ||
| الكثافة | 3.6452 kg/m3 (0 °C, 1013 mbar)[2] | ||
| نقطة الانصهار | |||
| نقطة الغليان | |||
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | 221 g/100 mL (0 °C) 204 g/100 mL (15 °C) 193 g/100 mL (20 °C) 130 g/100 mL (100 °C) | ||
| قابلية الذوبان | Soluble in alcohol, organic solvents | ||
| ضغط البخار | 2.308 MPa (at 21 °C) | ||
| الحموضة (pKa) | −8.8 (±0.8);[3] ~−9[4] | ||
| القاعدية (pKb) | ~23 | ||
| معامل الانكسار (nD) | 1.325[بحاجة لمصدر] | ||
| البنية | |||
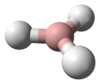
| الشكل الجزيئي | Linear | ||
| Dipole moment | 820 mD | ||
| الكيمياء الحرارية | |||
| الإنتالپية المعيارية للتشكل ΔfH |
−36.45...−36.13 kJ/mol[5] | ||
| Standard molar entropy S |
198.696–198.704 J/(K·mol)[5] | ||
| سعة الحرارة النوعية، C | 350.7 mJ/(K·g) | ||
| المخاطر | |||
| صفحة بيانات السلامة | hazard.com | ||
| ن.م.ع. مخطط تصويري |  
| ||
| ن.م.ع. كلمة الاشارة | Danger | ||
| H314, H335 | |||
| P261, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |||
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |||
| الجرعة أو التركيز القاتل (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (التركيز الأوسط)
|
2858 ppm (rat, 1 h) 814 ppm (mouse, 1 h)[7] | ||
| حدود التعرض الصحية بالولايات المتحدة (NIOSH): | |||
PEL (المسموح)
|
TWA 3 ppm (10 mg/m3)[6] | ||
REL (الموصى به)
|
TWA 3 ppm (10 mg/m3)[6] | ||
IDLH (خطر عاجل)
|
30 ppm[6] | ||
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |||
مركـّبات ذات علاقة
|
Hydrogen fluoride Hydrogen chloride Hydrogen iodide Hydrogen astatide | ||
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |||
| مراجع الجدول | |||
بروميد الهيدروجين Hydrogen bromide غاز عديم اللون يتبخر في الهواء الرطب.صيغته الكيميائية H Br ويمكن تحضيره بتفاعل الهيدروجين (H) مع البروم (Br) مباشرة أو بمعالجة أحد أملاح(HBr) مثل بروميد الصوديوم (NaBr) بحمض قوي غير متطاير. ويُسمى محلول بروميد الهيدروجين في الماء حمض الهيدروبروميك ويُستخدم كل من غاز بروميد الهيدروجين (HBr) ومحلوله المائي في صنع مركبات عضوية عديدة.
استخدامات بروميد الهيدروجين
Hydrogen bromide and hydrobromic acid are important reagents in the production of inorganic and organic bromine compounds.[8] The free-radical addition of HBr to alkenes gives alkyl bromides:
- RCH=CH2 + HBr → R−CHBr−CH3
These alkylating agents are precursors to fatty amine derivatives. Similar free radical addition to allyl chloride and styrene gives 1-bromo-3-chloropropane and phenylethylbromide, respectively.
Hydrogen bromide reacts with dichloromethane to give bromochloromethane and dibromomethane, sequentially:
- HBr + CH2Cl2 → HCl + CH2BrCl
- HBr + CH2BrCl → HCl + CH2Br2
Allyl bromide is prepared by treating allyl alcohol with HBr:
- CH2=CHCH2OH + HBr → CH2=CHCH2Br + H2O
تفاعلات أخرى
Although not widely used industrially, HBr adds to alkenes to give bromoalkanes, an important family of organobromine compounds. Similarly, HBr adds to haloalkene to form a geminal dihaloalkane. (This type of addition follows Markovnikov's rule):
- RC(Br)=CH2 + HBr → RC(Br2)−CH3
HBr also adds to alkynes to yield bromoalkenes. The stereochemistry of this type of addition is usually anti:
- RC≡CH + HBr → RC(Br)=CH2
Also, HBr is used to open epoxides and lactones and in the synthesis of bromoacetals. Additionally, HBr catalyzes many organic reactions.[9][10][11][12]
استخدامات محتملة
HBr has been proposed for use in a utility-scale flow-type battery.[13]
التحضير الصناعي
Hydrogen bromide (along with hydrobromic acid) is produced by combining hydrogen and bromine at temperatures between 200 and 400 °C. The reaction is typically catalyzed by platinum or asbestos.[10][14]
التحضير في المعمل
HBr can be synthesized by a variety of methods. It may be prepared in the laboratory by distillation of a solution of sodium bromide or potassium bromide with phosphoric acid or sulfuric acid:[15]
- KBr + H2SO4 → KHSO4 + HBr
Concentrated sulfuric acid is less effective because it oxidizes HBr to bromine:
- 2 HBr + H2SO4 → Br2 + SO2 + 2 H2O
The acid may be prepared by:
- reaction of bromine with water and sulfur:[15]
- 2 Br2 + S + 2 H2O → 4 HBr + SO2
- bromination of tetralin:[15]
- C10H12 + 4 Br2 → C10H8Br4 + 4 HBr
- reduction of bromine with phosphorous acid:[10]
- Br2 + H3PO3 + H2O → H3PO4 + 2 HBr
Anhydrous hydrogen bromide can also be produced on a small scale by thermolysis of triphenylphosphonium bromide in refluxing xylene.[9]
Hydrogen bromide prepared by the above methods can be contaminated with Br2, which can be removed by passing the gas through a solution of phenol at room temperature in tetrachloromethane or other suitable solvent (producing 2,4,6-tribromophenol and generating more HBr in the process) or through copper turnings or copper gauze at high temperature.[14]
السلامة
HBr is highly corrosive and irritating to inhalation.
المراجع
- ^ "Hydrobromic Acid - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 10 November 2011.
- ^ قالب:GESTIS
- ^ Trummal, Aleksander; Lipping, Lauri; Kaljurand, Ivari; Koppel, Ilmar A; Leito, Ivo (2016). "Acidity of Strong Acids in Water and Dimethyl Sulfoxide". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 120 (20): 3663–9. Bibcode:2016JPCA..120.3663T. doi:10.1021/acs.jpca.6b02253. PMID 27115918.
- ^ Perrin, D. D. Dissociation constants of inorganic acids and bases in aqueous solution. Butterworths, London, 1969.
- ^ أ ب Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
- ^ أ ب ت NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards 0331
- ^ "Hydrogen bromide". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Dagani, M. J.; Barda, H. J.; Benya, T. J.; Sanders, D. C. "Bromine Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a04_405.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|authors=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ أ ب Hercouet, A.; LeCorre, M. (1988) Triphenylphosphonium bromide: A convenient and quantitative source of gaseous hydrogen bromide. Synthesis, 157–158.
- ^ أ ب ت Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements; Butterworth-Heineman: Oxford, Great Britain; 1997; pp. 809–812.
- ^ Carlin, William W. U.S. Patent 4٬147٬601, April 3, 1979.
- ^ Vollhardt, K. P. C.; Schore, N. E. Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function; 4th Ed.; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY; 2003.
- ^ http://www1.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/pdfs/30535ag.pdf
- ^ أ ب Ruhoff, J. R.; Burnett, R. E.; Reid, E. E. "Hydrogen Bromide (Anhydrous)" Organic Syntheses, Vol. 15, p. 35 (Coll. Vol. 2, p. 338).
- ^ أ ب ت M. Schmeisser "Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 282.
- Articles with unsourced statements from November 2011
- Articles with changed EBI identifier
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles with changed KEGG identifier
- Articles with changed FDA identifier
- مقالات ذات عبارات بحاجة لمصادر
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chembox image size set
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- مركبات غير عضوية
- مركبات الهيدروجين
- بروميدات
- هاليدات لافلزية