إشعاع تراهرتس
في الفيزياء، يتألف إشعاع تراهرتز terahertz radiation من موجات كرومغناطيسية منتشرة على هيئة ترددات في حيز تراهرتز
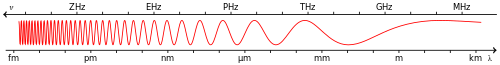
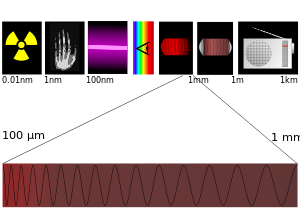
ويتراوح تردد موجات أشعة تيراهيرتز بين 0.3 تيراهيرتز إلى 3 تيراهيرتز. وتيرا سابقة تعني 1012. أي أن تيرا هرتز تعني شعاعا كهرومغناطيسيا يبلغ تردده نحو 1012 في الثانية . هذا يعادل طول موجة قدره نحو 1 مليمتر .
تتميز هذه الموجات بصعوبة إنتاجها وصعوبة استقبالها وامتصاصها وبانعكاسها الشديد من قبل المعادن. تستخدم في الأغراض الطبية لعدم ضررها بالإنسان, وفي التصوير، والاتصالات قصيرة المدى, وعلم الأطياف . كما ظهرت تطبيقات جديدة لهذه الأمواج في اكتشاف الأسلحة المخبأة تحت الملابس حيث تتميز هذه الأشعة بقدرتها على اختراق المنسوجات والبلاستيك والتقاط صور دقيقة للجسم عبر الملابس، وهو ما وضع استخدام هذه الأشعة موضع جدل.
من الطرق المتبعة لتوليد هذه الأمواج هو ضخ غاز الميثان باشعة تحت الحمراء، ومن الطرق أيضا عن طريق البصريات غير الخطية، واستخدام المزج الضوئي، واستخدام الهوائيات المهيجة باستخدام النبضات الضوئية القصيرة.
مقدمة

المصادر
- the gyrotron
- the backward wave oscillator ("BWO")
- the far infrared laser ("FIR laser")
- quantum cascade laser
- the free electron laser (FEL)
- synchrotron light sources
- photomixing sources
- single-cycle sources used in terahertz time domain spectroscopy such as photoconductive, surface field, photo-Dember and optical rectification emitters.
- In 2012, a source was announced that used a resonant tunnelling diode (RTD) in which the voltage decreased as the current increased, causing the diode to "resonate" and produce waves in the terahertz band at 542 GHz,
الأبحاث
- التصوير الطبي:
- Contrary to X-rays, terahertz radiation has a relatively low photon energy for damaging tissues and DNA. Some frequencies of terahertz radiation can penetrate several millimeters of tissue with low water content (e.g., fatty tissue) and reflect back. Terahertz radiation can also detect differences in water content and density of a tissue. Such methods could allow effective detection of epithelial cancer with a safer and less invasive or painful system using imaging.
- Some frequencies of terahertz radiation can be used for 3D imaging of teeth and may be more accurate than conventional X-ray imaging in dentistry.
- الأمن:
- Terahertz radiation can penetrate fabrics and plastics, so it can be used in surveillance, such as security screening, to uncover concealed weapons on a person, remotely. This is of particular interest because many materials of interest have unique spectral "fingerprints" in the terahertz range. This offers the possibility to combine spectral identification with imaging. Passive detection of terahertz signatures avoid the bodily privacy concerns of other detection by being targeted to a very specific range of materials and objects.[1][2]
- الاستخدام الطبي والتصوير:
- Spectroscopy in terahertz radiation could provide novel information in chemistry and biochemistry.
- Recently developed methods of THz time-domain spectroscopy (THz TDS) and THz tomography have been shown to be able to perform measurements on, and obtain images of, samples that are opaque in the visible and near-infrared regions of the spectrum. The utility of THz-TDS is limited when the sample is very thin, or has a low absorbance, since it is very difficult to distinguish changes in the THz pulse caused by the sample from those caused by long-term fluctuations in the driving laser source or experiment. However, THz-TDS produces radiation that is both coherent and spectrally broad, so such images can contain far more information than a conventional image formed with a single-frequency source.
- Submillimeter waves are used in physics to study materials in high magnetic fields, since at high fields (over about 11 tesla), the electron spin Larmor frequencies are in the submillimeter band. Many high-magnetic field laboratories perform these high-frequency EPR experiments, such as the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory (NHMFL) in Florida.
- Submillimetre astronomy.
- Terahertz radiation could let art historians see murals hidden beneath coats of plaster or paint in centuries-old buildings, without harming the artwork.[3]
- الاتصالات:
- Potential uses exist in high-altitude telecommunications, above altitudes where water vapor causes signal absorption: aircraft to satellite, or satellite to satellite.
- Manufacturing:
- Many possible uses of terahertz sensing and imaging are proposed in manufacturing, quality control, and process monitoring. These in general exploit the traits of plastics and cardboard being transparent to terahertz radiation, making it possible to inspect packaged goods.
رقم قياسي لسرعة نقل المعلومات
في مايو 2012، نشر باحثون في معهد طوكيو للتكنولوجيا[4] في رسائل إلكترونية عن تسجيلهم رقم قياسي جديد في سرعة نقل البيانات لاسلكياً باستخدام إشعاع هرتز واقترحوا استخدامها كسعة اتصال لنقل البيانات في المستقبل.[5] The team's proof of concept device used a resonant tunnelling diode (RTD) in which the voltage decreased as the current increased, causing the diode to "resonate" and produce waves in the terahertz band. With this RTD, the researchers sent a signal at 542 GHz, resulting in a data transfer rate of 3 Gigabits per second.[5] The demonstration was twenty times faster than the current Wi-Fi standard[5] and doubled the record for data transmission set the previous November.[6] The study suggested that Wi-Fi using the system would be limited to approximately 10 متر (33 ft), but could potentially allow data transmission at up to 100 Gbit/s.[5]
موجات تراهرتز وموجات سبميليمتر
The terahertz band, covering the wavelength range between 0.1 and 1 mm, is identical to the submillimeter wavelength band. However, typically, the term "terahertz" is used more often in marketing in relation to generation and detection with pulsed lasers, as in terahertz time domain spectroscopy, while the term "submillimeter" is used for generation and detection with microwave technology, such as harmonic multiplication.[بحاجة لمصدر]
الأمان
The terahertz region is between the radio frequency region and the optical region generally associated with lasers. Both the IEEE RF safety standard[7] and the ANSI Laser safety standard[8] have limits into the terahertz region, but both safety limits are based on extrapolation. It is expected that effects on tissues are thermal in nature and, therefore, predictable by conventional thermal models. Research is underway to collect data to populate this region of the spectrum and validate safety limits.
A study published in 2010 and conducted by Boian S. Alexandrov and colleagues at the Center for Nonlinear Studies at Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico[9][10] performed mathematical models how terahertz radiation interact with double-stranded DNA, showing that, even though involved forces seem to be tiny, nonlinear resonances (although much less likely to form than less-powerful common resonances) could allow terahertz waves to "unzip double-stranded DNA, creating bubbles in the double strand that could significantly interfere with processes such as gene expression and DNA replication".[11] Experimental verification of this simulation was not done. A recent analysis of this work concludes that the DNA bubbles do not occur under reasonable physical assumptions or if the effects of temperature are taken into account.[12]
انظر أيضاً
- ماسح الجسم الكامل
- Heterojunction bipolar transistor
- High electron mobility transistor (HEMT)
- Picarin
- Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy
المصادر
- ^ "Camera 'looks' through clothing". BBC News 24. 10 March 2008. Retrieved 10 March 2008.
- ^ ThruVision T5000 T-Ray Camera sees through Clothes
- ^ Hidden Art Could be Revealed by New Terahertz Device Newswise, Retrieved 21 September 2008.
- ^ K. Ishigaki, M. Shiraishi, S. Suzuki, M. Asada, N. Nishiyama, and S. Arai (10 May 2012). "Direct intensity modulation and wireless data transmission characteristics of terahertz-oscillating resonant tunnelling diodes". Electronic Letters. 48 (10): 582–3. Retrieved 16 May 2012.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ أ ب ت ث "Milestone for wi-fi with 'T-rays'". BBC News. 16 May 2012. Retrieved 16 May 2012.
- ^ Chacksfield, Marc (16 May 2012). "Scientists show off the future of Wi-Fi – smash through 3Gbps barrier". Tech Radar. Retrieved 16 May 2012.
- ^ IEEE C95.1–2005 , IEEE Standard for Safety Levels With Respect to Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields, 3 kHz to 300 GHz
- ^ ANSI Z136.1–2007, American National Standard for Safe Use of Lasers
- ^ "Los Alamos Scientist: TSA Scanners Shred Human DNA". Macedonian International News Agency. 17 December 2010. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ Alexandrov, B. S. ; Gelev, V. ; Bishop, A. R. ; Usheva, A. ; Rasmussen, K. O. (2010). "DNA Breathing Dynamics in the Presence of a Terahertz Field". Physics Letters A. 374 (10): 1214–1217. arXiv:0910.5294. Bibcode:2010PhLA..374.1214A. doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2009.12.077.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "How Terahertz Waves Tear Apart DNA". Technology Review. 30 October 2010. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ قالب:Cite arxiv
قراءات إضافية
- Quasioptical Systems: Gaussian Beam Quasioptical Propagation and Applications, Paul F. Goldsmith, IEEE Press (1997)
- Sensing with Terahertz Radiation, ed. Daniel Mittleman, Springer (2002)
- Terahertz Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications, ed. Susan L. Dexheimer, CRC Press (2007)
- Principles of Terahertz Science and Technology, Yun-Shik Lee, Springer (2008)
- Introduction to THz Wave Photonics, Xi-Cheng Zhang and Jingzhou Xu, Springer (2009)
- Terahertz Technology: Fundamentals and Applications, Ali Rostami, Hassan Rasooli and Hamed Baghban, Springer (2011)