تحليل مكاني
(تم التحويل من Spatial analysis)
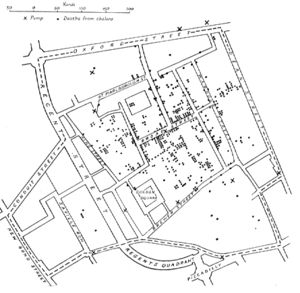
خريطة رسمها د. جون سنو من لندن، توضح تجمع حالات الكوليرا أثناء تفشي الكوليرا في برود ستريت 1854. وتعتبر هذه الخريطة من أوائل الاستخدامات للتحليل المكاني المعتمد على الخرائط.
التحليل المكاني Spatial analysis أو الإحصائيات المكانية spatial statistics، تشمل أي تقنيات رسمية تدرس الكيانات باستخدام خصائصها الطبولوجية، الهندسية، أو الجغرافية. يشمل التحليل المكاني مختلف التقنيات، لا يزال الكثير منها في مراحل تطوره المبكرة، ويستخدم المنهاج التحليلة المهتلفة ويطبقها في مجالات مختلفة من الفلك، ودراساته الخاصة بوضع المجرات في الكون، حتى هندسة تصنيع الرقاقات، واستخدامها لوغاريتمات "المكان والمسار" لبناء هياكل الأسلاك المعقدة. بشكل أكثر تحديداً، التحليل المكني هو التقنية المطبقة على الهياكل في النطاق الإنساني، ومن أشهرها تحليل البيانات الجغرافية.
تاريخ التحليل المكاني
قضايا أساسية في التحليل المكاني
التوصيف المكني
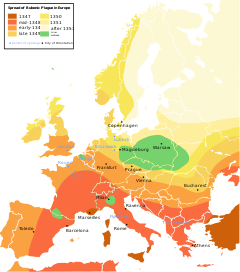
Spread of bubonic plague in medieval Europe.[citation needed] The colors indicate the spatial distribution of plague outbreaks over time. Possibly due to the limitations of printing or for a host of other reasons, the cartographer selected a discrete number of colors to characterize (and simplify) reality.
التبعية المكانية أو الارتباط الذاتي
التدرج
أخذ العينات
الأخطاء الشائعة في التحليل المكني
حلول للقضايا الأساسية

Manhattan distance versus Euclidean distance: The red, blue, and yellow lines have the same length (12) in both Euclidean and taxicab geometry. In Euclidean geometry, the green line has length 6×√2 ≈ 8.48, and is the unique shortest path. In taxicab geometry, the green line's length is still 12, making it no shorter than any other path shown.
أنواع التحليل المكاني
تحليل البيانات المكنية
التبعية الذاتية المكانية
الاستيفاء المكاني
الانحدار المكاني
التفاعل المكاني
المحاكاة والنمذجة
الاحصائيات الجغرافية متعددة النقاط
علم المعلومات الجغرافية والتحليل المكاني

This flow map of Napoleon's ill-fated march on Moscow is an early and celebrated example of geovisualization. It shows the army's direction as it traveled, the places the troops passed through, the size of the army as troops died from hunger and wounds, and the freezing temperatures they experienced.
المحتوى
انظر أيضاً
- موضوعات عامة
- رسم الخرائط
- Complete spatial randomness
- GeoComputation
- Geospatial predictive modeling
- Dimensionally Extended nine-Intersection Model (DE-9IM)
- علم المعلومات الجغرافية
- إحصائيات رياضية
- Modifiable Areal Unit Problem
- Spatial autocorrelation
- Spatial relation
- تطبيقات محددة
- نظم المعلومات الجغرافية
- Geodemographic segmentation
- Visibility analysis
- Fuzzy architectural spatial analysis
- Suitability analysis
- Extrapolation domain analysis
- Geoinformatics
- Boundary problem (in spatial analysis)
- Spatial epidemiology
- Spatial econometrics
المصادر
قراءات إضافية
- Abler, R., J. Adams, and P. Gould (1971) Spatial Organization–The Geographer's View of the World, Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- Anselin, L. (1995) "Local indicators of spatial association – LISA". Geographical Analysis, 27, 93–115.
- Banerjee, S., B.P. Carlin and A.E. Gelfand (2004). Hierarchical Modeling and Analysis for Spatial Data. Taylor and Francis: Chapman and Hall/CRC Press.
- Benenson, I. and P. M. Torrens. (2004). Geosimulation: Automata-Based Modeling of Urban Phenomena. Wiley.
- Fotheringham, A. S., C. Brunsdon and M. Charlton (2000) Quantitative Geography: Perspectives on Spatial Data Analysis, Sage.
- Fotheringham, A. S. and M. E. O'Kelly (1989) Spatial Interaction Models: Formulations and Applications, Kluwer Academic
- Fotheringham, A. S.; Rogerson, P. A. (1993). "GIS and spatial analytical problems". International Journal of Geographical Information Systems. 7: 3–19. doi:10.1080/02693799308901936.
- Goodchild, M. F. (1987). "A spatial analytical perspective on geographical information systems" (PDF). International Journal of Geographical Information Systems. 1: 327–44. doi:10.1080/02693798708927820.
- MacEachren, A. M. and D. R. F. Taylor (eds.) (1994) Visualization in Modern Cartography, Pergamon.
- Levine, N. (2010). CrimeStat: A Spatial Statistics Program for the Analysis of Crime Incident Locations. Version 3.3. Ned Levine & Associates, Houston, TX and the National Institute of Justice, Washington, DC. Ch. 1-17 + 2 update chapters [1]
- Miller, H. J. (2004). "Tobler's First Law and spatial analysis". Annals of the Association of American Geographers. 94: 284–289. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8306.2004.09402005.x.
- Miller, H. J. and J. Han (eds.) (2001) Geographic Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, Taylor and Francis.
- O'Sullivan, D. and D. Unwin (2002) Geographic Information Analysis, Wiley.
- Parker, D. C., S. M. Manson, M.A. Janssen, M. J. Hoffmann and P. Deadman (2003) "Multi-agent systems for the simulation of land-use and land-cover change: A review". Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 93, 314–337.
- White, R.; Engelen, G. (1997). "Cellular automata as the basis of integrated dynamic regional modelling". Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design. 24: 235–246. doi:10.1068/b240235.
- Scheldeman, X. & van Zonneveld, M. (2010). Training Manual on Spatial Analysis of Plant Diversity and Distribution. Bioversity International.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Fisher MM, Leung Y (2001) Geocomputational Modelling: techniques and applications. Springer Verlag, Berlin
- Fotheringham, S; Clarke, G; Abrahart, B (1997). "Geocomputation and GIS". Transactions in GIS. 2: 199–200. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9671.1997.tb00010.x.
- Openshaw S and Abrahart RJ (2000) GeoComputation. CRC Press
- Diappi L (2004) Evolving Cities: Geocomputation in Territorial Planning. Ashgate, England
- Longley PA, Brooks SM, McDonnell R, Macmillan B (1998), Geocomputation, a primer. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
- Ehlen, J; Caldwell, DR; Harding, S (2002). "GeoComputation: what is it?". Comput Environ and Urban Syst. 26: 257–265. doi:10.1016/s0198-9715(01)00047-3.
- Gahegan, M (1999). "What is Geocomputation?". Transaction in GIS. 3: 203–206. doi:10.1111/1467-9671.00017.
- Murgante B., Borruso G., Lapucci A. (2009) "Geocomputation and Urban Planning" Studies in Computational Intelligence, Vol. 176. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
- Fischer M., Leung Y. (2010) "GeoComputational Modelling: Techniques and Applications" Advances in Spatial Science. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
- Murgante B., Borruso G., Lapucci A. (2011) "Geocomputation, Sustainability and Environmental Planning" Studies in Computational Intelligence, Vol. 348. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
- Tahmasebi, P.; Hezarkhani, A.; Sahimi, M. (2012). "Multiple-point geostatistical modeling based on the cross-correlation functions" (PDF). Computational Geosciences. 16 (3): 779–79742. doi:10.1007/s10596-012-9287-1.
- Tóth, G., Kincses, Á., Nagy, Z., (2014) European Spatial Structure LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing, ISBN 978-3-659-64559-4, DOI:10.13140/2.1.1560.2247
وصلات خارجية
- ICA Commission on Geospatial Analysis and Modeling
- An educational resource about spatial statistics and geostatistics
- A comprehensive guide to principles, techniques & software tools
- Social and Spatial Inequalities
- National Center for Geographic Information and Analysis (NCGIA)
- International Cartographic Association (ICA), the world body for mapping and GIScience professionals
This article contains content from Wikimedia licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Please comply with the license terms.