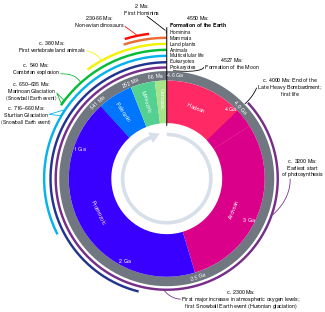
التاريخ الجيولوجي للأرض
بدأ التاريخ الجيولوجي للأرض منذ 4.567 بليون سنة [1] عندما تشكلت كواكب المجموعة الشمسية من السديم الشمسي، حيث شكلت مخلفات الشمس كتلة من الغبار والغازات. في البداية كانت الأرض عبارة عن كتلة منصهرة ثم بدأت القشرة الخارجية تبرد، عندما بدأت المياه تتجمع في الغلاف الجوي. وتشكل القمر بعد ذلك ، ربما كنتيجة لوجود فرق بين كتلة المريخ والأرض بحوالي 10%،[2]
التاريخ الجيولوجي للأرض follows the major geological events in Earth's past based on the geological time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.
Initially, the Earth was molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as a result of the impact of a planetoid with the Earth. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans. However, in 2020, researchers reported that sufficient water to fill the oceans may have always been on the Earth since the beginning of the planet's formation.[3][4][5]
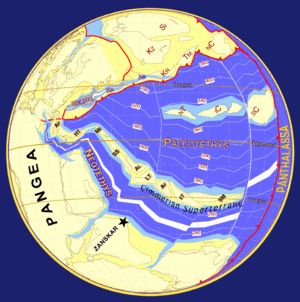
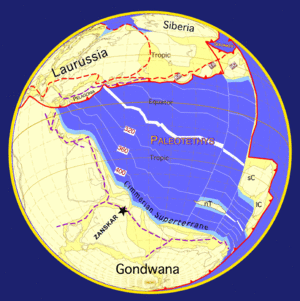
As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly , the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, , then finally Pangaea, which broke apart .
The present pattern of ice ages began about , then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thawing, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.
ويمكن تصنيف التاريخ الجيولوجي للأرض إلى عصرين: قبل الكمبري ، والفانروزوي.
ما قبل الكمبري
يتضمن العصر قبل الكمبري حوالي 90% من الزمن الجيولوجي. ويمتد ذلك العصر لفترة 4.6 بليون سنة مضت حتى بداية العصر الكمبري (حوالي 570 عام). The Precambrian includes approximately 90% of geologic time. It extends from 4.6 billion years ago to the beginning of the Cambrian Period (about 539 Ma). It includes the first three of the four eons of Earth's prehistory (the Hadean, Archean and Proterozoic) and precedes the Phanerozoic eon.[7]
Major volcanic events altering the Earth's environment and causing extinctions may have occurred 10 times in the past 3 billion years.[8]
ويتضمن ثلاث عصور جيولوجية:
عصر هاديان

During Hadean time (4.6–4 Ga), the Solar System was forming, probably within a large cloud of gas and dust around the sun, called an accretion disc from which Earth formed .[1] The Hadean Eon is not formally recognized, but it essentially marks the era before we have adequate record of significant solid rocks. The oldest dated zircons date from about .[9][10][11]

Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as a result of the impact of a large planetoid with the Earth.[12][13] More recent potassium isotopic studies suggest that the Moon was formed by a smaller, high-energy, high-angular-momentum giant impact cleaving off a significant portion of the Earth.[14] Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.[15] However, in 2020, researchers reported that sufficient water to fill the oceans may have always been on the Earth since the beginning of the planet's formation.[3][4][5]
During the Hadean the Late Heavy Bombardment occurred (approximately ) during which a large number of impact craters are believed to have formed on the Moon, and by inference on Earth, Mercury, Venus and Mars as well. However, some scientists argue against this hypothetical Late Heavy Bombardment, pointing that the this conclusion has been drawn from data which are not fully representative (only a few crater hotspots on the Moon have been analyzed).[16][17]
عصر أرشين
Proterozoic Eon
Phanerozoic Eon
Paleozoic Era
العصر الكمبري
العصر الاردوڤيشي
Silurian Period
Devonian Period
العصر الكربوني
العصر الپرمي
العصر الوسيط
العصر الترياسي
العصر الجوراسي
العصر الطباشيري

الدهر الحديث
Paleogene Period
Paleocene Epoch
العصر الايوسيني
Oligocene Epoch
The Oligocene epoch extends from about 34 Ma (ICS 2004) to 23 Ma (ICS 2004).
Neogene Period
العصر الميوسيني
العصر الپليوسيني
العصر الپليستوسيني
Holocene Epoch
المصادر
- ^ أ ب Dalrymple, G.B. (1991). The Age of the Earth. California: Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-1569-6. خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صالح؛ الاسم "age_earth" معرف أكثر من مرة بمحتويات مختلفة. - ^ Canup, R. M.; Asphaug, E. (Fall Meeting 2001). "An impact origin of the Earth-Moon system". Abstract #U51A-02, American Geophysical Union. Retrieved on 2007-03-10.
- ^ أ ب Piani, Laurette (28 August 2020). "Earth's water may have been inherited from material similar to enstatite chondrite meteorites". Science. 369 (6507): 1110–1113. Bibcode:2020Sci...369.1110P. doi:10.1126/science.aba1948. PMID 32855337. S2CID 221342529. Retrieved 28 August 2020.
- ^ أ ب Washington University in St. Louis (27 August 2020). "Meteorite study suggests Earth may have been wet since it formed - Enstatite chondrite meteorites, once considered 'dry,' contain enough water to fill the oceans -- and then some". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 28 August 2020.
- ^ أ ب American Association for the Advancement of Science (27 August 2020). "Unexpected abundance of hydrogen in meteorites reveals the origin of Earth's water". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 28 August 2020.
- ^ Merdith, Andrew (16 December 2020). "Plate tectonics, Rodinia, Gondwana, supercontinent cycle". Plate model for 'Extending Full-Plate Tectonic Models into Deep Time: Linking the Neoproterozoic and the Phanerozoic'. doi:10.5281/zenodo.4485738. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
- ^ Nisbet, E.G. (1991-12-01). "Of clocks and rocks - The four aeons of Earth". Episodes (in الإنجليزية). 14 (4): 327–330. doi:10.18814/epiiugs/1991/v14i4/003. ISSN 0705-3797.
- ^ Witze, Alexandra. "Earth's Lost History of Planet-Altering Eruptions Revealed". Scientific American (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2017-03-14.
- ^ Gradstein, Felix M.; Ogg, James G.; Smith, Alan G., eds. (2004). A geologic time scale 2004. Cambridge University Press. p. 145. ISBN 9780521786737.
- ^ "International Chronostratigraphic Chart v.2015/01" (PDF). International Commission on Stratigraphy. January 2015.
- ^ Wilde, S. A.; Valley, J.W.; Peck, W.H.; Graham, C.M. (2001). "Evidence from detrital zircons for the existence of continental crust and oceans on the Earth 4.4 Gyr ago". Nature. 409 (6817): 175–178. Bibcode:2001Natur.409..175W. doi:10.1038/35051550. PMID 11196637. S2CID 4319774.
- ^ (2001) "An impact origin of the Earth-Moon system"., American Geophysical Union.
- ^ Canup, RM; Asphaug, E (2001). "Origin of the Moon in a giant impact near the end of the Earth's formation". Nature. 412 (6848): 708–712. Bibcode:2001Natur.412..708C. doi:10.1038/35089010. PMID 11507633. S2CID 4413525.
- ^ Wang, K.; Jacobsen, S.B. (Sep 12, 2016). "Potassium isotopic evidence for a high-energy giant impact origin of the Moon". Nature. 538 (7626): 487–490. Bibcode:2016Natur.538..487W. doi:10.1038/nature19341. PMID 27617635. S2CID 4387525.
- ^ Morbidelli, A.; Chambers, J.; Lunine, Jonathan I.; Petit, J. M.; Robert, F.; Valsecchi, G. B.; Cyr, K. E. (2000). "Source regions and time scales for the delivery of water to Earth". Meteoritics & Planetary Science. 35 (6): 1309–1320. Bibcode:2000M&PS...35.1309M. doi:10.1111/j.1945-5100.2000.tb01518.x.
- ^ Brasser, R.; Mojzsis, S.J.; Werner, S.C.; Matsumura, S.; Ida, S. (December 2016). "Late veneer and late accretion to the terrestrial planets". Earth and Planetary Science Letters (in الإنجليزية). 455: 85–93. arXiv:1609.01785. Bibcode:2016E&PSL.455...85B. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2016.09.013. S2CID 119258897.
- ^ Mojzsis, Stephen J.; Brasser, Ramon; Kelly, Nigel M.; Abramov, Oleg; Werner, Stephanie C. (2019-08-12). "Onset of Giant Planet Migration before 4480 Million Years Ago". The Astrophysical Journal. 881 (1): 44. arXiv:1903.08825. Bibcode:2019ApJ...881...44M. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab2c03. hdl:10852/76601. ISSN 1538-4357. S2CID 84843306.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
وصلات خارجية
- Cosmic Evolution — a detailed look at events from the origin of the universe to the present
- Valley, John W. “A Cool Early Earth?” Scientific American. 2005 Oct:58–65. – discusses the timing of the formation of the oceans and other major events in Earth’s early history.
- Davies, Paul. “Quantum leap of life”. The Guardian. 2005 Dec 20. – discusses speculation into the role of quantum systems in the origin of life
- Evolution timeline (uses Shockwave). Animated story of life since about 13,700,000,000 shows everything from the big bang to the formation of the earth and the development of bacteria and other organisms to the ascent of man.
- Scientific American Magazine (October 2005 Issue) A Cool Early Earth?
- Artist's Conception of Cold Early Earth
- Theory of the Earth
- Theory of the Earth & Abstract of the Theory of the Earth