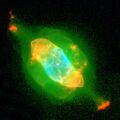
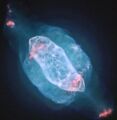
سديم زحل
| Saturn Nebula | |
|---|---|
 NGC 7009 by Very Large Telescope.[1] | |
| Observation data (Epoch J2000.0) | |
| Right ascension | 21س 04د 10.877ث[2] |
| Declination | −11° 21′ 48.25″[2] |
| Distance | 2000-4000 ly (See article) |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.0[3] |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 41″ × 35″[2] |
| Constellation | Aquarius |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Radius | 0.2 to 0.4 |
| Absolute magnitude (V) | 2.5 to 1 |
| Notable features | - |
| Other designations | NGC 7009,[2] Caldwell 55 |
| See also: Planetary nebula, Lists of nebulae | |
سديم زحل (Saturn Nebula ؛ ويُعرف أيضاً باسم NGC 7009 أو كالدوِل 55) هو سديم كوكبي في كوكبة الدلو. ويظهر على شكل صبغة صفراء مخضرة في تلسكوب هواة صغير. اكتشفه وليام هرشل في 7 سبتمبر 1782 ، باستخدام منظار من تصميمه الخاص في الحديقة بمنزله في داتشت، إنگلترة، وكان من أوائل اكتشافاته في مسح السماء. كان السديم في الأصل نجم منخفض الكتلة يقذف طبقاته إلى الفضاء ويشكل السديم. النجم المركزي هو الآن نجم قزم أبيض بحجم ظاهري 11.5. اشتق اسم سديم زحل من تشابهه السطحي مع كوكب زحل حيث تقترب حلقاته من حافة الراصد. تم تسميته بهذا الاسم من قبل اللورد روس في أربعينيات القرن التاسع عشر، عندما تحسنت التلسكوبات لدرجة أنه يمكن تمييز شكلها الشبيه بزحل. قال وليام هنري سميث أن سديم زحل كان واحداً من أجرام ستروفه "السماوية النادرة" التسع.[4]
The Saturn Nebula is a complex planetary nebula and contains many morphological and kinematic sub-systems in three dimensions. It includes a halo, jet-like streams, multiple shells, ansae ("handles"), and small-scale filaments and knots. The ansae are expanding non-radially from the central star.[5] Although the ansae are most prominent in the Saturn Nebula, they are also visible in other planetary nebulae, including NGC 3242, NGC 6543 and NGC 2371-2.
The distance of the Saturn Nebula is not known precisely. Sabbadin et al. 2004 estimates the distance to be 5,200 light-years (1.6 kpc). In 1963 O'Dell estimated it to be 3,900 light-years (1.2 kpc), which gives an approximate diameter of 0.5 light years for the object as a whole.
The central star, a very hot bluish dwarf with a temperature of 55,000 K, from which the nebula is believed to originate, has an absolute magnitude of +1.5, which equates to a luminosity of about 20 solar luminosities and a visual magnitude of 11.5. This strong ultraviolet irradiation from the central star creates the characteristic fluorescent green tint of the nebula via the radiation of doubly ionized oxygen. The object overall has a visual magnitude of 8 and a radial velocity of 28 miles per second towards the Earth.
The nebula is 1 degree west of the star Nu Aquarii. The central portion measures 25″ × 17″, while the outer shell extends to 41″ × 35″. The object is on many "best of" observing lists.[6][7]
معرض
NGC 7009 by Hubble Space Telescope.
1848 drawing of NGC 7009 by Lord Rosse.
This visualisation shows three-dimensional MUSE data of the nebula.
الهامش
- ^ "The Strange Structures of the Saturn Nebula". www.eso.org. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
- ^ أ ب ت ث "NAME Saturn Nebula". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2006-12-26.
- ^ "Messier Online Astronomical Database". Saturn Nebula. Retrieved 2012-08-28.
- ^ "NGC 7009, the Saturn Nebula". www.messier.seds.org. Retrieved 2020-12-26.
- ^ Steffen, W.; Espíndola, M.; Martínez, S.; Koning, N. (October 2009). "The 3D velocity structure of the planetary nebula NGC 7009". Revista Mexicana de Astronomía y Astrofísica. 45: 143–54. arXiv:0905.2148. Bibcode:2009RMxAA..45..143S.
NGC 7009 is a planetary nebula with several morphological and kinematical sub-systems with multiple shells, a halo, jet-like streams, ansae and small-scale filaments and knots.
- ^ SAC 110 best NGC object list
- ^ RASC's Finest N.G.C. Objects O[http://messier.seds.org/xtra/similar/caldwell.html The Caldwell Catalog (#55)
المراجع
- Sabbadin, Franco; Turatto, M.; Cappellaro, E.; Benetti, S.; Ragazzoni, R. (March 2004). "The 3-D ionization structure and evolution of NGC 7009 (Saturn Nebula)". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 416 (3): 955–81. arXiv:astro-ph/0312261. Bibcode:2004A&A...416..955S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20031729.
وصلات خارجية
| سديم زحل
]].- NASA APOD (1997-12-30) – NGC 7009: The Saturn Nebula
- The Saturn Nebula on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images