تصوير عصبي
(تم التحويل من التصوير العصبي)
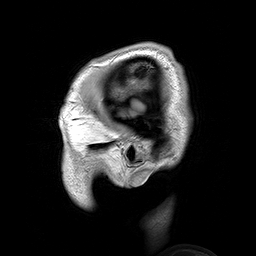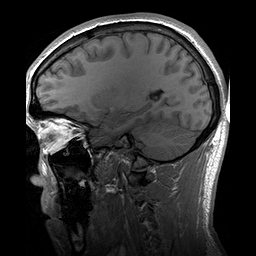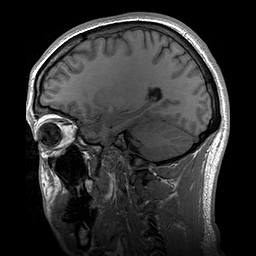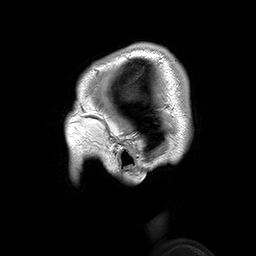
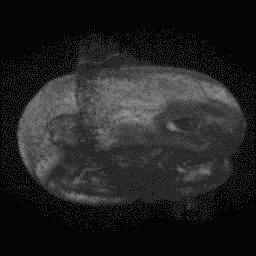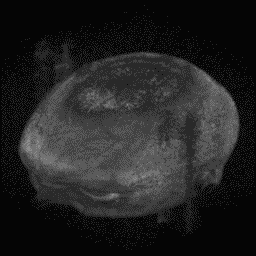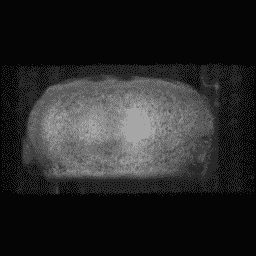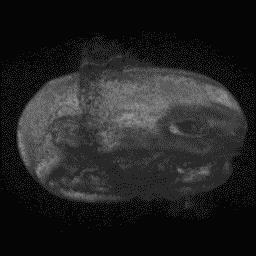
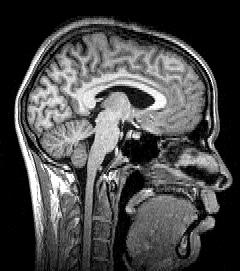
Para-sagittal MRI of the head in a patient with benign familial macrocephaly.
التصوير العصبي Neuroimaging، يتضمن استخدام تقنيات مختلفة للتصوير المباشر أو الغير مباشر للبنية، الوظيفة/علم عقاقير المخ. وهو فرع جديد نسبيا في الطب وعلم الأعصاب/علم النفس.[1]
نظرة عامة
يقسم التصوير العصبي إلى فئتين:
- تصوير بنيوي، والذي يتعامل مع بنية المخ وتشخيص إجمالي (واسع النطاق) للأمراض القحفية (مثل الأورام)، الجروح.
- التصوير الوظيفي، والذي يستخدم لتشخيص الأمراض الأيضية والأضرار واسعة النطاق (مثل مرض ألزهامير) وأيضا في أبحاث علم النفس المعرفي والعصبي وبناء brain-computer interface.
ويمكن للتصوير الوظيفي، على سبيل المثال، معالجة المعلومات عن طريق مراكز في المخ ليتم تصويرها مباشرة. مثل معالجة المنطقة المصابة في المخ والمسئولة عن زيادة الأيضا والتي تظهر مضيئة في المسح. وأحد الاستخدامات المعرفية للتصوير الوظيفي هي استخدامه في التعرف على الأفكار أو قراءة الفكر.
التاريخ
تقنيات تصوير المخ
التصوير المقطعي المحور
التصوير البصري المتفرق
أحداث مرتبطة بالإشارة الضوئية
التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي
التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي الوظيفي
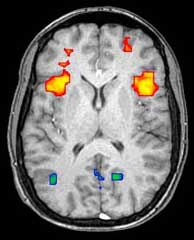
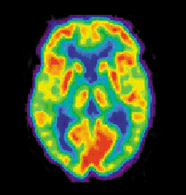
Axial MRI slice at the level of the basal ganglia, showing fMRI BOLD signal changes overlayed in red (increase) and blue (decrease) tones.
Electroencephalography
Magnetoencephalography
Positron emission tomography
Single photon emission computed tomography
انظر أيضا
- Brain mapping
- تصوير عصبي وظيفي
- functional near-infrared imaging
- تاريخ تصوير المخ
- Human Cognome Project
- تصوير بالرنين المغناطسي
- Magnetoencephalography
- تصوير طبي
- قائمة قاعدة بيانات العلوم العصبية
- برمجيات التصوير العصبي
- Statistical parametric mapping
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation
- Voxel-based morphometry
المصادر
- ^ Filler, AG: The history, development, and impact of computed imaging in neurological diagnosis and neurosurgery: CT, MRI, DTI: Nature Precedings DOI: 10.1038/npre.2009.3267.5.Neurosurgical Focus (in press)
قراءات إضافية
- Philip Ball. Brain Imaging Explained.
- J. Graham Beaumont (1983). Introduction to Neuropsychology. New York: The Guilford Press.
- Jean-Pierre Changeux (1985). Neuronal Man: The Biology of Mind. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Malcom Jeeves (1994). Mind Fields: Reflections on the Science of Mind and Brain. Grand Rapids, MI: Baker Books.
- Richard G. Lister and Herbert J. Weingartner (1991). Perspectives on Cognitive Neuroscience. New York: Oxford University Press.
- James Mattson and Merrill Simon (1996). The Pioneers of NMR and Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. United States: Dean Books Company.
- Lars-Goran Nilsson and Hans J. Markowitsch (1999). Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory. Seattle: Hogrefe & Huber Publishers.
- Donald A. Norman (1981). Perspectives on Cognitive Science. New Jersey: Ablex Publishing Corporation.
- Brenda Rapp (2001). The Handbook of Cognitive Neuropsychology. Ann Arbor, MI: Psychology Press.
- Berger, H. (1929). Über das Elektroenkephalogramm des Menschen. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. 87(1), 527:570.
وصلات خارجية
مشاع المعرفة فيه ميديا متعلقة بموضوع Category:Neuroimaging.
- The Whole Brain Atlas @ Harvard
- The McConnell Brain Imaging Center, McGill University
- The American Society of Neuroimaging (ASN).
- UCLA Neuroimaging Training Program.
- Laboratory of Neuro Imaging at UCLA
- A Neuroimaging portal
- BrainMapping.org, a free BrainMapping community information portal
- Lecture notes on mathematical aspects of neuroimaging by Will Penny, University College London
- "Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation". by Michael Leventon in association with MIT AI Lab.
- Foundations of fMRI by Jamie Shorey.
- International Society for Neuroimaging in Psychiatry (ISNIP)
- Journal of Neuroimaging
- Neuromorphometrics- manual mri labeling
This article contains content from Wikimedia licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Please comply with the license terms.