نيستاتين
نستاتين نستاتين هو polyene antifungal drug ,أغلب الفطريات molds و الخميرة yeast حساسة له, تشمل فصائل candida و نستاتين له سمية إذا أعطى حقنا في الوريد ولكنه لا يمتص من خلال الجلد السليم أو الأغشية المخاطية, ويعد آمنا نسبيا لعلاج الإلتهابات الفطرية الفموية والمعوية .
 | |
| البيانات السريرية | |
|---|---|
| فئة السلامة أثناء الحمل |
|
| مسارات الدواء | topical & oral (but not absorbed) |
| رمز ATC | |
| الحالة القانونية | |
| الحالة القانونية |
|
| بيانات الحركية الدوائية | |
| التوافر الحيوي | 0% on oral ingestion |
| الأيض | ? |
| Elimination half-life | ? |
| الإخراج | ? |
| المعرفات | |
| |
| رقم CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.317 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
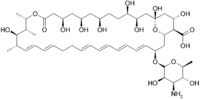
| التركيب | C47H75NO17 |
| الكتلة المولية | 926.09 |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الإستعمالات
الإلتهابات الجلدية , و المهبلية ,التهابات المرىء وفصائل الكانديدا كلها تستجيب جيدا للعلاج بالنستاتين , Cryptococcus حساس أيضا للنستاتين.فى المملكة المتحدة , تم حظر إستخدامه للطفح الفمي لدى الرضع الذين يزيد عمرهم عن شهر, وأستبدل ب (miconazole younger babies). [بحاجة لمصدر] ويستعمل نستاتين كوقائى ضد الإلتهابات الفطرية لدى مصابى الأيدز AIDS with a low CD4+ count and patients receiving chemotherapy. وجرعاته تحسب بالوحدات وتتراوح مابين 100.000 الى مليون وحدة في العدوى المعوية, وحيث أنه لايمتص من الأمعاء, فهو آمن للإستعمال عن طريق الفم, ولامشاكل له إذا أستعمل مع أدوية أخرى.
It is also used in cellular biology as an inhibitor of the lipid raft-caveolae endocytosis pathway on mammalian cells, at concentrations around 3 µg/mL.
In certain cases, Nystatin has been used to prevent the spread of mold on objects such as works of art. For example, it was applied to wood panel paintings damaged as a result of the Arno River Flood of 1966 in Florence, Italy.
Nystatin is also used as a tool by scientists performing "perforated" patch-clamp electrophysiologic recordings of cells. When loaded in the recording pipette, it allows for measurement of electrical currents without washing out the intracellular contents, because it forms pores in the cell membrane that are permeable to only monovalent ions.[1]
نظرية العمل
Like amphotericin B and natamycin, nystatin binds to ergosterol, a major component of the fungal cell membrane. When present in sufficient concentrations, it forms pores in the membrane that lead to K+ leakage and death of the fungus. Ergosterol is fairly unique to fungi, so the drug does not have such catastrophic effects on animals.
الأصل
Like many other antifungals and antibiotics, nystatin is of bacterial origin. It was isolated from Streptomyces noursei in 1950 by Elizabeth Lee Hazen and Rachel Fuller Brown, who were doing research for the Division of Laboratories and Research of the New York State Department of Health. The soil sample where they discovered nystatin was from the garden of Hazen's friends called Nourses, therefore the strain was called noursei. Hazen and Brown named nystatin after the نيويورك State Public Health Department (now known as the Wadsworth Center) in 1954.
الأسماء التجارية
- Nystan (oral tablets, topical ointment, and pessaries, Bristol-Myers Squibb)
- Infestat
- Nystalocal
- Nystamont
- Nystop (topical powder, Paddock)
- Nystex
- Mykinac
- Nysert (vaginal suppositories, Procter & Gamble)
- Nystaform (topical cream, and ointment and cream combined with iodochlorhydroxyquine and hydrocortisone; formerly Bayer now Typharm Ltd)
- Nilstat (vaginal tablet, Lederle)
- Korostatin (vaginal tablets, Holland Rantos)
- Mycostatin (vaginal tablets, topical powder, Bristol-Myers Squibb)
- Mycolog-II (topical ointment, combined with triamcinolone; Apothecon)
- Mytrex (topical ointment, combined with triamcinolone)
- Mykacet (topical ointment, combined with triamcinolone)
- Myco-Triacet II (topical ointment, combined with triamcinolone)
- Flagystatin II (cream, combined with metronidazole)
- Nistatina (oral tablets, Antibiotice Iaşi)
- Nidoflor (cream, combined with neomycin sulfate and triamcinolone acetonide, Antibiotice Iaşi)
المراجع
- ^ Akaike N, Harata N. (1994) Nystatin perforated patch recording and its applications to analyses of intracellular mechanisms. Jpn J Physiol, 44(5):433-73; PMID 7534361.